Skip to main content
Link
Menu
Expand
(external link)
Document
Search
Copy
Copied
# Introduction ## CSE513: Fall 2025 Jennifer Mankoff 2025-08-07 Important Reminder: check zoom & captioning <a href="/courses/cse513/25au/slides/introduction.html">Live View: /slides/introduction.html</a><br> <a href="/courses/cse513/25au/slides/introduction.html"><img src="https://api.qrserver.com/v1/create-qr-code/?data=/slides/introduction.html&size=100x100" alt="QR for /courses/cse513/25au/slides/introduction.html" title="" /></a> --- class: center, middle, inverse # Announcements -- ## [No Announcements Today] --- class: center, middle, inverse # Introductions --- ## Jennifer Mankoff (they/she) [Make4All Lab](make4all.org) | [CREATE](create.uw.edu) I use technology to improve inclusion in and accessibility of our digital future. That includes research, but also who succeeds in academia. <img alt="Photograph of a white person with curly brown hair and glasses on their head in a blue shirt learning on a railing" src="../assets/images/mankoff.jpg" class="fitheight"> --- ## Lucille Njoo I'm a PhD student with a disability working on ethics in NLP. I also do a lot of disability advocacy, such as running the student group Ability. My service dog's name is CeCe! <img alt="Photo of an Asian woman with a black ponytail pointing to something off screen and kneeling on the ground next to a tan-and-black service dog with crooked ears" src="../assets/images/njoo.jpg" class="fitheight"> --- ## Warm up <iframe src="https://embed.polleverywhere.com/free_text_polls/cAlcFAh68Z0Bz2xOe1Twl?controls=none&short_poll=true" width="800px" height="600px"></iframe> --- ## Introduce yourselves Discuss with at least two neighbors: Do you know whether your favorite app is inclusive of one or more of the following. What does inclusion mean in an app? - Race - Gender - Disability <!-- {% include qr.html url=site.discussion %} --> <!-- {% include qr.html %} --> <!-- {% include qr.html url=site.discussion %} --> <!-- {% capture discussion %} --> <!-- site.discussion --> <!-- {% endcapture %} --> <!-- {% include qr.html url=discussion %} --> --- class: center, middle, inverse # Today's learning goals --- ## Course learning goals (1/5) 1. **Familiarity with a range of Accessibility Technologies** --- ## AT today is readily available There are lots of tutorials It's on every device You will learn just enough to be dangerous! - Information about how the AT works, users, and strengths and weaknesses of the AT. - Information about what disabilities can benefit from it. For example, screen readers are not just used by blind people. - General comfort using it to assess accessibility --- ## Course learning goals (2/5) 1. Familiarity with a range of Accessibility Technologies 2. **Accessible Document Creation** 3. **Accessible Presenting** 4. **Plain Language** --- ## How you share your work must be accessible - ALT text for images - Best practices for Word and PowerPoint accessibility - Automated accessibility checking - Best practices in live presentations - Best practices for plain language --- ## Course learning goals (3/5) 1. Familiarity with a range of Accessibility Technologies 2. Accessible Document Creation 3. Accessible Presenting 4. Plain Language 5. **Disability Model Analysis** --- ## Critical Viewpoints on Disability Work 1. Understanding how to apply critical models 2. Recognizing ableism & other tropes --- ## Course learning goals (4/5) 1. Familiarity with a range of Accessibility Technologies 2. Accessible Document Creation 3. Accessible Presenting 4. Plain Language 5. Disability Model Analysis 6. **Finding First-Person Accounts of Accessibility Tech** --- ## Disability Leadership in Selecting Problems - First person accounts get us close - Community-engaged work is the real goal --- ## Learning Goals ≡ Competencies We use *competency based grading* because it prioritizes *accessibility* and *justice* and *flexibility* for students. **Traditional grading** focuses on completion of required tasks | 85% projects | 15% participation | |--------------|--------------------------| | *project 1* | *class attendance* | | project 2 | asking question in class | | ... | ... | --- ## What is competency-based grading? **Competency-based grading** focuses on evidence of progress and learning | learning goal 1 | learning goal 2 | learning goal 3 | |------------------------------|---------------------|----------------------------| | *Evidence: Project 1* | Evidence: Project 1 | Evidence: Project 2 | | *Evidence: Project 2* | Evidence: Project 3 | Evidence: Project 4 | | *Evidence: Final Project* | | Evidence: Discussion post | | ... | ... | ... | -- Teaching and learning are centered around *learning outcomes*. This changes how we plan, assess and grade the course. --- class: center, middle, inverse # Defining Disability ---  --- ## Disability is a context-dependent mismatch .left-column50[ **1980**  **A personal attribute** *"restriction or lack of ability ... within the range considered normal for a human being"* (medical model: How do we *fix people*) ] .left-column50[ **1990s** 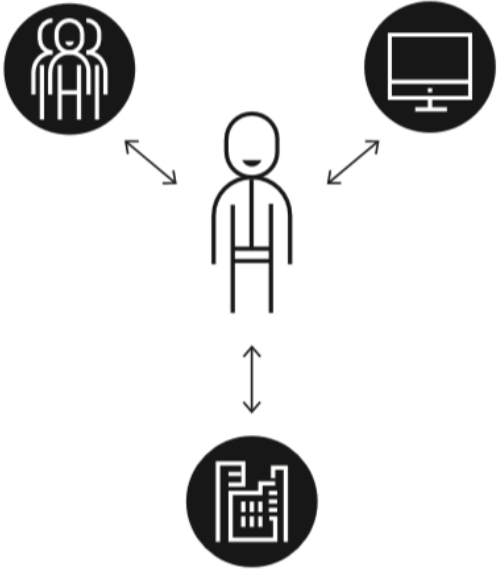 **A social/environmental attribute** *"the interaction between features of a person's body and features of the society in which they live"* (social model: how do we *fix society*) ] ??? **Disability as a personal attribute** "restriction or lack of ability ... within the range considered normal" Older views (1980s). This **medical model** asks how do we *fix people*: **Disability as a societal consequence** "the interaction between features of a person's body and ... [their] society" More recent views (2000s). This **social model** asking how do we *fix society* --- ## Neither is quite right - Medical Model: how do we fix people <!-- .element: class="fragment" --> - Social Model: how do we fix society <!-- .element: class="fragment" --> - Postmodern—Disability doesn't need to be fixed. Disability is celebrated as part of human variation. Disability pride, disability culture, and disabled joy are all things to support and celebrate. <!-- .element: class="fragment" --> --- ## Worldwide Stats | || | || | |--------|---------|----------------|--------|----------|---------------| | BVI | DHH | Neurodiverse | Speech | Mobility | Mental Health | | Ray Charles | Marlee Matlin | Temple Grandin | President Biden | Ali Stroker | Catherine Zeta-Jones| | *Colorblind*<BR>*Visual Impairment*<BR>*Blind* | *Hearing loss* <BR> *Deaf* | *Dyslexia* <BR> *Autism* <BR> *PTSD* | *Stutter* <BR> *Nonspeaking* <BR> *Dyspraxia* | *Quadriplegia* <BR> *Limb different* | *Bipolar*<BR>*Anxiety*<BR>*PTSD*<BR>*Depression* | ??? 1 Billion (~15%) of population [WHO'11]; 19% of USA [Census'12] call out that you don't have to be famous to be proud of being disabled call out multiple disabilities --- ## Rates of Disability are increasing Rates of disability are increasing - Aging population - Long COVID - Increasing numbers of people with chronic illness (can span disability segments) Not everyone in these groups identifies as disabled --- ## Don't oversimplify - People can be multiply disabled - More than one disabled person might be in the same space with different accommodations - Intersectionality with Race, Gender & other identities --- exclude: true --- ## Accommodation Accommodation is your right - Co-producing access for all participants in a space or event - Sometimes helped by software & media, some [free](https://depts.washington.edu/uwdrs/technology/) - Legally mandated, but also so much more - Mandated by multiple laws in Higher Education (That is why UW has a DRS office) - Ongoing and constant legal challenges, especially to the [ADA](http://www.webaim.org/coordination/law/us/ada) ??? 147 countries have ratified the **UN Convention on Rights of PD** (2006) 1996 ADA complaint against San José Use of PDF inaccessible to city commissioner Web sites are a “service” and thus subject to the ADA Led to S. J. Web Page Disability Access Standard 1999 Natn’l Fed. of the Blind against AOL Based on the interpretation of the Web as a place of public accommodation (ADA) Settled out of court 2000: AOL agreed to make its browser accessible Many others (http://www.webaim.org/coordination/law/us/ada) --- ## Some US laws - **Individuals with Disabilities Education Act** (IDEA, 1975)--Free appropriate public education in the least restrictive environment to every child with a disability. - Section 503 of the **Rehab Act** (1973)--Equal access to government services - **Americans with Disabilities Act** (1990)--Equal access to all goods/services --- ## Accessibility Research is more than accommodation - Multi person systems - Mobile systems - Data Equity: Visualization and Machine Learning - Making Accessibility: Fabrication and IOT - AR/VR - Sustainability - Housing, Unhoused, and Incarcerated - Healthcare technology & reproductive justice - Higher Education - ... --- class: center, middle, inverse # Class Access Norms & Syllabus --- ## How is this class accessible? (1/3) Many disabilities benefit from flexibility in how time is spent -- - Up to two late days *per assignment* for assignment completion, no questions asked - If you need further accommodations for any reason, talk to us and consider working with [DRS](https://depts.washington.edu/uwdrs/) as well. - Multiple opportunities to try competencies → Where possible, we provide those as a standard part of the class. --- <iframe src="https://embed.polleverywhere.com/discourses/xJbn0rf9y5vH6DgBBTxrM?controls=none&short_poll=true" width="800px" height="600px"></iframe> --- ## Small Group Discussion How would you implement this in your lab or workplace? --- ## How is this class accessible? (2/3) Sometimes students with disabilities, such as chronic illness or mental health concerns may need to participate in class remotely. Other students (and your instructor) may have higher risk for COVID. -- - Please attend class remotely if you have an access need, a cold, flu, or suspected COVID symptoms. - Same for a disability accommodation We will *work to ensure* you have an equal experience. Outside of this, or travel, **in-person attendance is expected** --- <!-- .slide: data-visibility="hidden" --> ## How do I receive participation credit when remote? 1. You arrange for a zoom buddy ahead of class 2. You *attend via Zoom* with the help of your zoom buddy 3. You *participate meaningfully in that day's in-class activities* 4. You *report how your participation went* using the [reporting form](https://forms.gle/3g5GXZscUgvFtES76) --- ## How is this class accessible? (3/3) We commit to mutually working together to make it accessible. - DRS approval is required for some accommodations (specifically, those that are not available to the entire class) - But many accommodations benefit most students. → where possible, we provide those as a standard part of the class. ??? This is a form of *disability justice* Why disability justice? because access to disability documentation and comfort with disclosure are both things that are inequitably distributed --- <iframe src="https://embed.polleverywhere.com/discourses/xJbn0rf9y5vH6DgBBTxrM?controls=none&short_poll=true" width="800px" height="600px"></iframe> --- ## Access is also for the teaching staff Once you learn how to make the course more accessible to the teaching staff, please do. - Turn in accessible documents for grading (e.g. you should always provide ALT text for your images and captioned videos). - Communicate through the discussion board or mailing list rather than emailing us individually - Support us and each other in creating access for the whole class --- class: center, middle, inverse # Class Structure --- ## Weekly Rhythm **Monday**: Lecture; Reading questions due **Wednesday**: Critique and HW for critique due **Friday**: HW out and some HW due --- ## Other Important Facts about this Class - **Language**: I am Jen (preferred), or Dr. Mankoff or Prof. Mankoff - **Religious Holidays**: Let me know if they will impact your participation - **Inclusivity**: An important value in this class, and in HCI! --- ## A little more on Inclusivity - Inclusivity does not (and should not) require disclosure, this goes for accessibility and ANYTHING else - How can you ask for help without violating privacy or boundaries? I won't make you justify your requests for help or accommodations or pry into your life. - Especially because Biden's new Title IX regulations make me a mandatory reporter. ??? This is the most important thing I’m going to talk about today. --- ## A Note on Academic Integrity Don't plagiarize. If you use text, quote it and reference it. Sharing is fine, but don't copy from each other. See our [syllabus](../syllabus.html) page for more details Why? UW policy and [*Citational Justice*](https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-022-00793-1) and thus an important expression of disability justice values in our class. --- ## GAI rules 1/2 You may use GAI for assignments and exams unless I specify that it may not be used or other guidelines. However: - Cite the AI program you used in the artifact you hand in - If it copies text or closely copies ideas from other sources, you must cite those sources - Do not use generative AI to plagiarize or cheat. For example, you may not use AI to create fake data and pass that off as based on real people. --- ## GAI rules 2/2 You will be held to the same standards when you use generative AI as for any assignment, regardless of whether you or the AI created something, including: - If you turn in artifacts that are not accessible, you will be graded accordingly - If you turn in assignments based on ableist claims - If you turn in artifacts that contain false or incomplete claims, you will be graded accordingly - You will be graded based on critical thinking and writing skills. --- class: center, middle, inverse # Grading --- ## Competencies Competencies are your base grade and the core learning goals in this class. - We assess them twice each - The final assessment determines your grade - After you've completed a competency twice, you can request a regrade - If you learn them all well, you will do well in the class --- ## How Competencies Translate to Grades - On any competency, you may be rated as below competent, competent or excellent. - There are 6 competencies total - Your grade is calculated as an average of your competency scores, and converted to a 4.0 scale, with a max grade of 3.9 if you have all excellents --- ## Getting to excellent - Most students get "competent" or below on their first try - This usually goes up on the second try. - You can submit more tries if you want - You can submit regrade requests after your second try. --- ## Applied Effort Assignment completion and participation is required. - Non-completion can reduce your competency grade by up to 50% (if you complete no assignments) --- ## Final Project Competency Adjustment Final Project is also assessed on competencies - It can bring an individual competency score down by up to one point - Bringing a competency up requires and individually submitted re-assessment request and attestation regarding your individual contributions to that specific competency --- ## Engagement Engagement can bring a grade up by 0.05 (essentialy changes how it is rounded) - You need to collect 10 points to raise a grade by 0.05. You get to choose what works best for you. Examples: - Completing a small group activity - Completing an in-class assignment (such as laser cutting) - Reporting back to the room after a small group discussion in class - Helping a student out with something relevant to class such as how to use a screen reader - Leading a paper discussion in class --- ## Example of Student Competency (1/2) - The presentation slide deck for your first homework looks mostly accessible, however you ran out of time to use the accessibility checker. As a result, one of your images was missing ALT text, and the screen reader order was not great. you score "Not Competent" on accessible documents. - On your next assignment you take special care with image descriptions, but the document was so simple that you cannot demonstrate five different accessibility practices. You are marked "Competent" but the TA has some advice on how to be write more specific and useful descriptions. Even so, you recognize that a regrade request wouldn't change the outcome, so you decide to submit another slide deck later. --- ## Example of Student Competency (2/2) - The next time create a slide deck (as part of a final project checkpoint) you submit an individual version of it for review. This has all the pieces done correctly, and is complex enough to receive an "Excellent" <!-- .class="fragment" --> - You take responsibility for ensuring that other materials your group produces score excellent on accessible documens as well. This is a great way to practice your new skills and ensure that your competency score stays high. <!-- .class="fragment" --> --- class: center, middle, inverse # Assignments --- ## First Assignment: [AT Around Us](../assignments/finding-accessibility.html) (1/2) Competencies: Accessible Documents; First person Accounts - Find one computer access technology - Find one about "the world" - Find a description of it *by a disabled person who uses it* (first-person experience) - Should try at least one out yourself --- ## First Assignment: [AT Around Us](../assignments/finding-accessibility.html) (2/2) - Try not to pick the same things as your classmates - Should include a *first person video* - At least one should involve computers; - No disability dongles! Nothing too common (like glasses) --- ## Example 1: AAC - Many tablet apps exist that support communication for / by non-verbal people - Users include people with autism, neurological disabilities or with vocal injury might use these. Some users may have both speech and motor impairments that limit typingn - I would like to know how nonspeech aspects of communication are supported (humor, backchanneling, etc) --- ## Paired In class activity: Is it a first person account? [PollEv.com/jmankoff](http://PollEv.com/jmankoff) <iframe src="https://pollev-embeds.com/surveys/pMTUylxej5PgcR8KP3VMh/respond" width="800px" height="600px"></iframe> ??? - [No] AAC mealtime - The AAC user never addresses the audience - The AAC user never comments on the experience of using it - [No] Dynavox - It is highly scripted - It doesn't really review the device at hand - [Borderline] Street crossing - City-produced video with first person account (see 2:10) - Limitations: Not universally available; Does not support DeafBlind - Designed for people with visual impairments to cross the street - [Yes] Kit Autie --- ## First Person Account? (Ex 1) <iframe width="560" height="315" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/9FzbX1z-JAM?si=-6nHU5ndN72OH6h3" title="Integrating AAC device during Mealtime with nonverbal autism" frameborder="0" allow="accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share" referrerpolicy="strict-origin-when-cross-origin" allowfullscreen><span class="media-title-hidden">A mom describes how she is teaching her child to communicate using AAC at mealtimes</span></iframe> --- ## First Person Account? (Ex 2) <iframe width="560" height="315" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/tYgMfL-CnGo?si=-6nHU5ndN72OH6h3" title="Window to the world- Discover the I-Series communication device" frameborder="0" allow="accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share" referrerpolicy="strict-origin-when-cross-origin" allowfullscreen><span class="media-title-hidden"> An advertisement for the Tobii Dynavox</span></iframe> --- ## First Person Account? (Ex 3) <iframe width="560" height="315" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/z3YQ9F4SFAQ?si=-6nHU5ndN72OH6h3" title="Using AAC as an Autistic person" frameborder="0" allow="accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share" referrerpolicy="strict-origin-when-cross-origin" allowfullscreen><span class="media-title-hidden">A first person account of how Kit Autie uses AAC to communicate with a few different types of AAC</span></iframe> --- ## First Person Account? (Ex 4) <iframe width="560" height="315" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/xPlsYhU1HBU?si=jiklQmTbCUQHRcNI" title="Audible Crosswalk in Columbia, MO" frameborder="0" allow="accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share" referrerpolicy="strict-origin-when-cross-origin" allowfullscreen><span class="media-title-hidden">A first person account of reasons and factors using audible crosswalks</span></iframe> --- ## Results <iframe src="https://embed.polleverywhere.com/multiple_choice_polls/0PP88QZthghe6SMXWQ7uK?controls=none&short_poll=true" width="800px" height="600px"></iframe> --- ## Survey Results [Survey Results](https://www.polleverywhere.com/surveys/zbxQh4OxTDrtiZWOuF2KW) <iframe width="560" height="315" src="https://www.polleverywhere.com/surveys/zbxQh4OxTDrtiZWOuF2KW" title="Survey Results">Survey Results</iframe> --- ## Example 1: First Slide .column[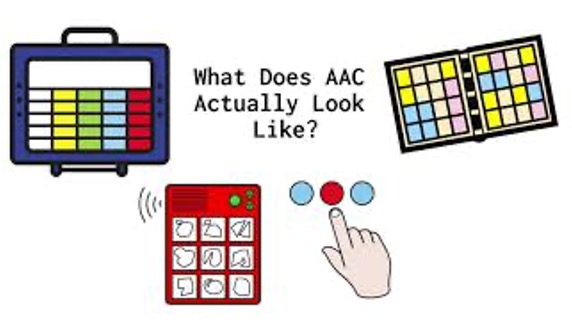] .doublecolumn[ - Many tablet apps exist that support communication for / by non-verbal people - People with autism, neurological disabilities or with vocal injury might use these. - Some users may have both speech and motor impairments that limit typing - I would like to know how nonspeech aspects of communication are supported (humor, backchanneling, etc) ] --- ## Example 1: First Person Account .column[<iframe ="560" height="315" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/z3YQ9F4SFAQ?si=-6nHU5ndN72OH6h3" title="Using AAC as an Autistic person" frameborder="0" allow="accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share" referrerpolicy="strict-origin-when-cross-origin" allowfullscreen><span class="media-title-hidden">A first person account of how Kit Autie uses AAC to communicate with a few different types of AAC</span></iframe> ] .doublecolumn[ - Kit Autie [describes why they use AAC and ableist reactions they get when using it](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=z3YQ9F4SFAQ) - Shows the variety of options available over specific strengths - I learned that "*languaging*" is a multi-person activity in which people can co-create access (or create ableism around access) - Costs have come way down!! (free with in-app purchases) ] --- ## Competencies for [AT Around Us](../assignments/finding-accessibility.html) - Accessible presentation creation - Finding first person accounts by and for people with disabilities - Presenting accessibly to an audience with mixed disabilities - Familiarity with a range of accessibility technologies Handin: - One accessible slide per AT (see [Ed](https://edstem.org/us/courses/87147/) for slide deck) - Reflection and List of Competencies on Canvas --- ## Other Homework - [Discussant](../assignments/discussant.html) -- a group leads paper discussion. First assignment will be used to sign you up, but we need at least 2 volunteers for next Wednesday! - Read assigned papers and post on [Ed](https://edstem.org/us/courses/87147/)--- you summarize a paper in a different week (individual) - [Research Paper Analysis](../assignments/paper-review.html) -- critical analysis of a research paper - [Accessibility Implementation](../assignments/technology-implementation.html) -- improve the accessibility of a thing - Final [Project](../projects.html) - (THIS WEEK!) fill out [Gradescope Absences and Syllabus Check Form](https://www.gradescope.com/courses/1131108/assignments/6807181)