as3: Accessibility
Last revised: Friday, January 29th, 2021- 27 January, 2021
- Due 4-Feb, 10:00pm
- Lock 6-Feb, 10:00pm
- Reflection 6-Feb, 10:00pm
- Reflection lock (with 10% deduction) 7-Feb, 10:00pm
Android Goals:
- Explore Android assistive tools
- Learn to read and modify someone's existing, relatively complex source code
- Repair accessibility issues in the codebase
HCI Goals:
- Experience App accessibility
- Understanding the impact of different accessibility issues
- Write up a report on accessiblity issues
GitGrade links
This assignment involves finding, fixing, and documenting all the accessibility problems in the code base for a revised version of the app AskforHelp (the original app can be found on the Android play store, and has been modified with permission). You will use a number of tools to find accessibilty issues with the App, including but not limited to the Google Accessibility Scanner and TalkBack. It will be important for you to experience the app through the use of a screen reader to find all of the problems a user might encounter.
- Note that it may be important to iterate through a find/fix cycle as fixing one accessibilty problem may uncover new ones.
- Also note that you should fix problems that users with a variety of disabilities might encounter (i.e. your app should be usable by someone with low vision, difficulty with motor control, or blindness)
This assignment is very different from other assignments in this class, because it will depend primarily on you using your judgement. You will have to explore your own ideas for how to make this app accessible and implement them using any approach you believe works. The proof will be in the pudding, so to speak: Would a reasonable person think that you have made the app accessible based on the screen/audio recording that you make?
Another reason this assignment is different is because you will need to read and understand someone else’s code to make the changes you want to make. The decisions they made will influence how you are able to solve accessibility problems, and you will need to think about where to modify their code. You do not need to write any new methods to solve the accessibility problems, or remove or add elements to the interface. You also don’t need to add any new event handlers. You will need to modify things like the content descriptions of on screen elements, whether they are focusable, and so on, and announce changes to the screen that are visible but not to a screen reader.
GitGrade links
Classroom Summary
Links: Accept the Assignment / Turn-in the Assignment
Tasks
Accessibility is an important part of any app. Whether you are developing a new app or adding features to an existing one, it is important to consider the accessibility of your app’s components.
In this assignment you will:
- Learn different categories of app accessibility issues
- Identify accessibility issues in AskforHelp
- Repair accessibility issues you identify
- Write a report
- Produce a video showing that your app is accessible
Your tasks are as follows:
- Do the background readings required for class
- Set up your phone with the accessibility tools and the AskforHelp app provided through gitgrade.
- Ensure it possible for anyone to complete the following four tasks using AskforHelp.
- Go to settings from the home screen and turn on location
- Add a request
- Choose a request, choose a contact, and send the request
- Delete a request
- Document the problems you fixed in your reflection. This will include providing all of the alt text that you add to the application.
- Make a video of yourself completing all four tasks, in order, using the screen reader, without looking at the screen.
1. Background Readings
Read (or watch) the following for background information:
- Read Principles for improving app accessibility
- Read about proper alt text writing.
- Read Make Apps more accessible
- Read Testing your app’s accessibility
Optional:
- Material Design’s Accessibility
- Epidemiology as a Framework for Large-Scale Mobile Application Accessibility Assessment
- Haben Girma on Disability and Innovation: The Universal Benefits of Accessible Design
- This quick video by Android’s Victor Tsaren will show you how visually-impaired users interact with Android applications. The video also offers some tips on ensuring your app is compatible with assistive tools.
- Android Accessibility Tutorial
- Starting Android Accessibility
2. Setup your phone and the app
Check your emulator
Ensure that your emulator have access to the Google Play Store. Emulators such as Pixel 2 allow you to install the Play Store using the Tools->AVD Manager. The best way to determine if the emulator has the Play Store is to look for the icon under the Play Store column in the AVD Manager.
To create another emulator, press the Create Virtual Device button, then find an emulator that has the Play Store icon in the Play Store column. Click Next and follow the instructions for the rest of the installation.
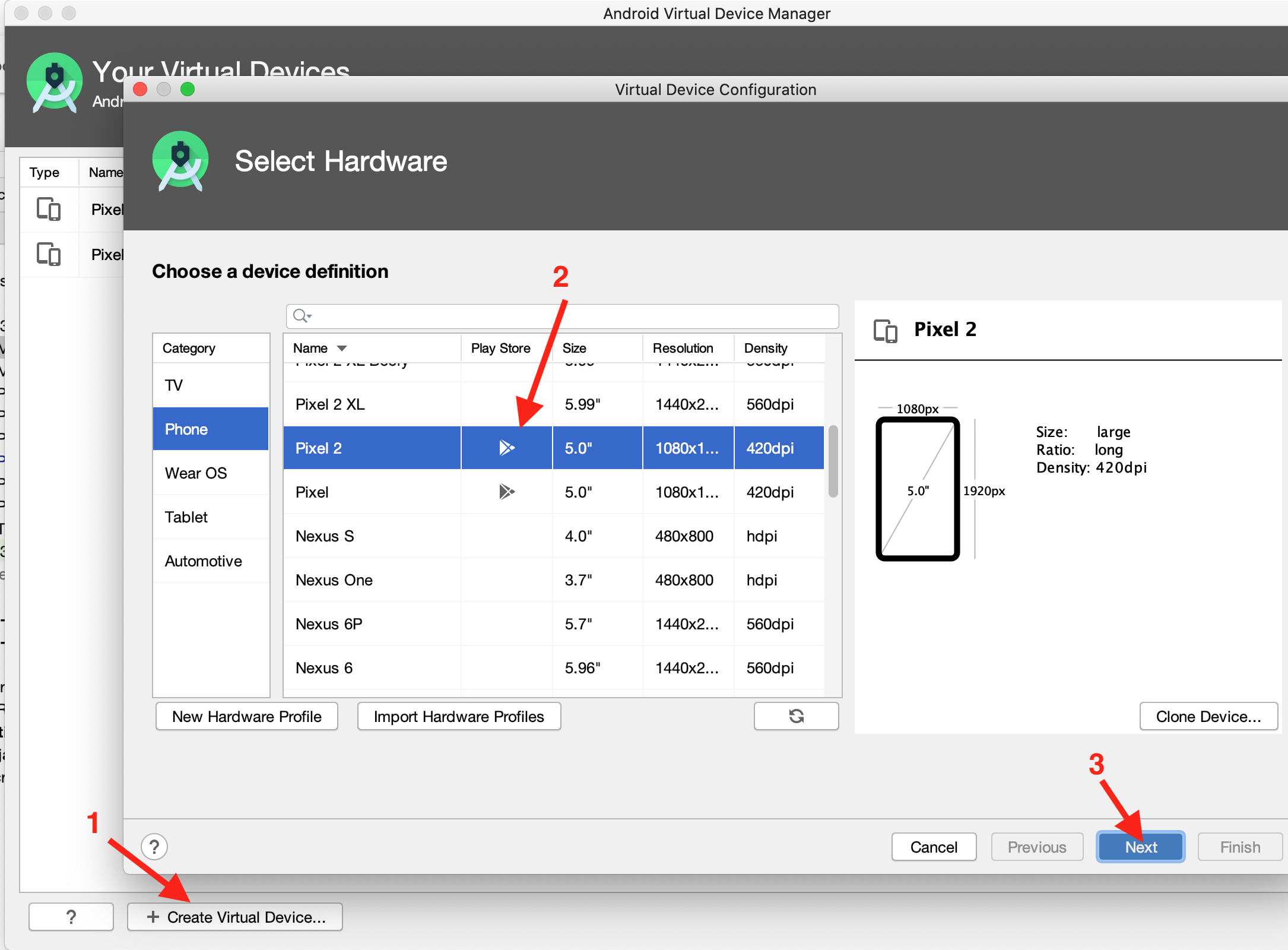
Note that you will have to specifically choose this new emulator (as opposed to the one you were using before) when you are running your application on the emulator through Android Studio.
Installing Assistive Technologies for testing
It will be necessary to test the user interface with Talkback, Android’s built in screen reader, to find all of the problems. Talkback is part of the Android Accessibility Suite and Android support provides a tutorial on how to install and use it talkback. Another assistive tool in this suite is Switch Access, which you may choose to explore.
To install the Android Accessibility Suite, search for it in the Play Store on your device or emulator and install it. The installation process will be the same for a physical phone or the emulator equiped with the Play Store.
Finally, install the Accessibility scanner. Follow the instructions on the Getting started with Google Accessibility Scanner page to get the scanner working on your device.
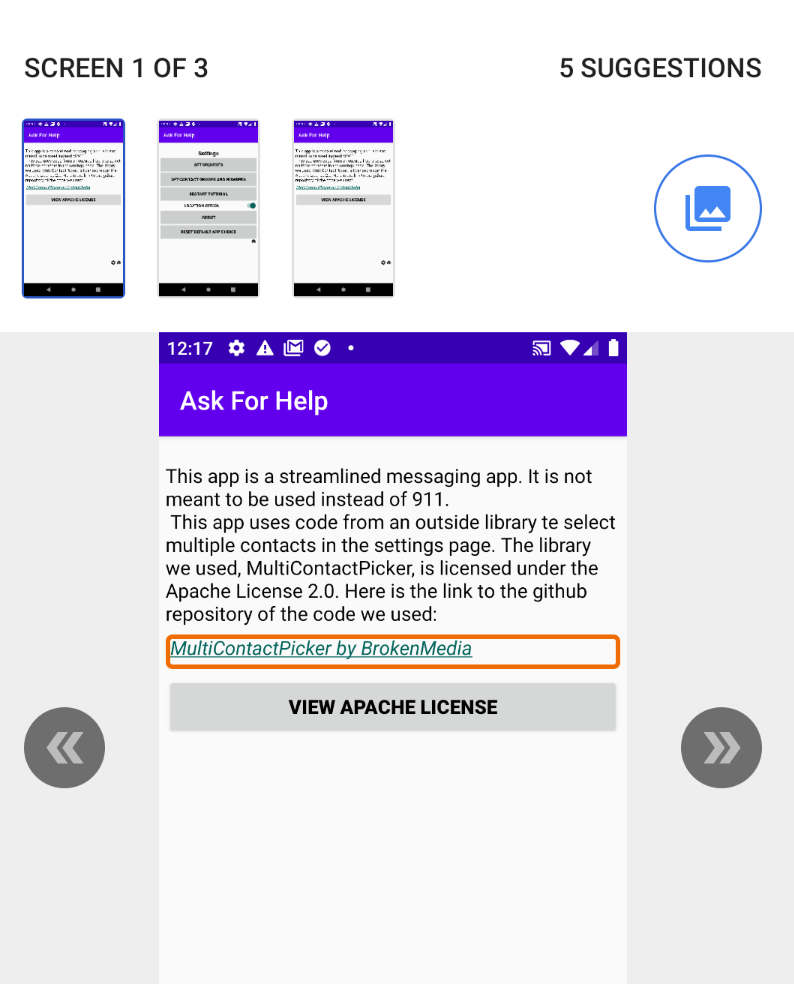
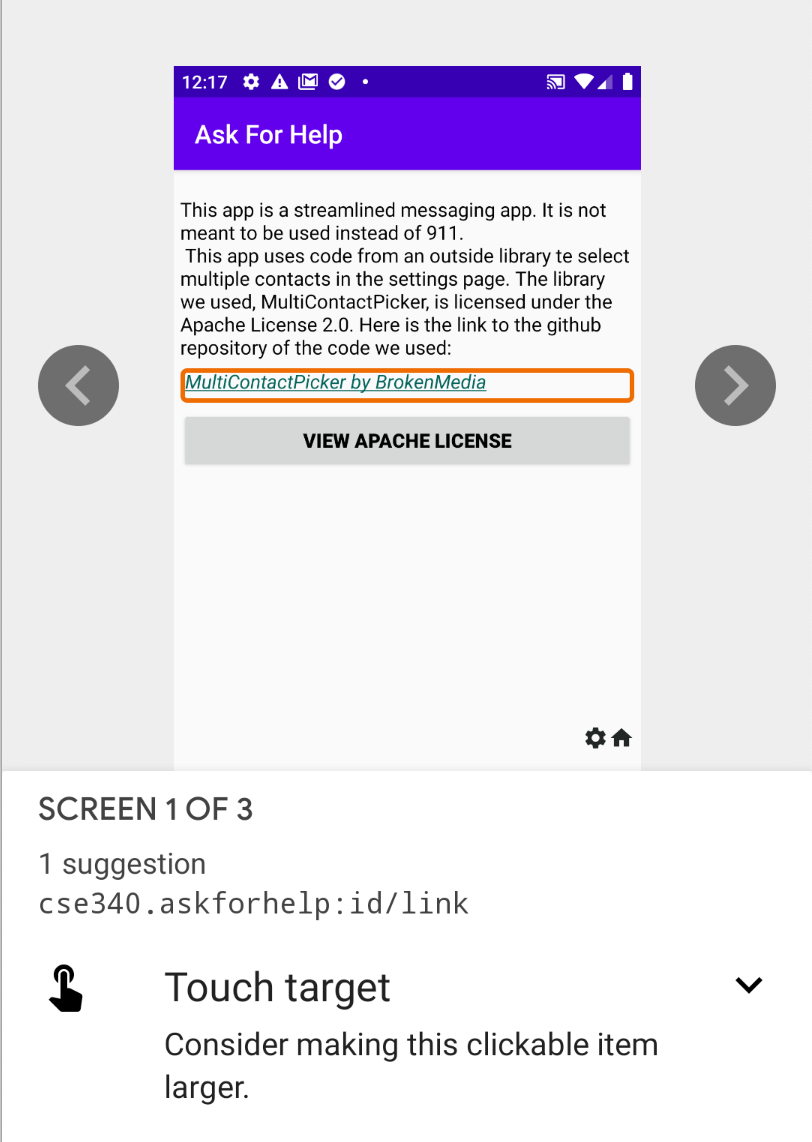
The Accessibility Scanner will show you information about some (but not all) accessibility problems. Below we show an example of what it finds on the About screen for AskforHelp.
| Accessibility Scanner | Focus on Problem item |
|---|---|
 |
 |
Install the Accessibility assignment code and try using it
Note: The first time you run the application (which we will refer to as AskforHelp) it will ask for permission to access your contacts and to access this device’s location. Please allow the app to do both of these things - you will not be able to test the app fully if you do not.
AskforHelp will show a tutorial when you run it. The goal of this application is to let people who have certain types of fatigue related disabilities to send text messages quickly and easily when they fall or become weak.
In order to work, the user has to preset some important messages (called Requests in the app) and one or more groups of contacts to whom messages will be sent. If the user turns on the Location on toggle in the AskforHelp settings, their GPS location will be included with the message.
Message requests and contacts are set up in AskforHelp through the Settings page. Setting up contact groups are a two step process - first the user gives the contact group a name, then they select which contacts to message from a contact manager in Android. You must make the screen where you set the contact group names accessible, but you do not need to make the contact picker accessible as we are using a 3rd party library for this functionality.
Note: In order to get the app to work correctly you must have at least one contact listed with a mobile number set up in your Android Contacts application. Thus you will need to create a contact or two if you are running on the emulator OR a physical mobile device.
Once the user has set up the requests and the contacts, they can set up a message with two clicks after opening the app. AskforHelp will open up your preferred text messaging app and pre-populate the message (along with location if that isturned on). To actually send the message the user would only need to press send in the messaging app.
To prepare your application you must add at least one request and at least one contact to it before your testing.
3. Make AskforHelp accessible
Now that you are set up, you will make the following four tasks accessible for anyone. Note that we are assuming you have already set up at least one contact (we are not including this in the list of tasks because it requires interacting with a different app to select the contact).
- Go to settings from the home screen and turn on location
- Add a request
- Choose a request, choose a contact, and send the request
- Delete a request
For example, it should be possible for someone with low vision or for someone using a screen reader who is swiping from interactor to interactor (rather than directly clicking on them) to complete these tasks using your accessible version of AskforHelp.
You should start by trying each of these tasks without any changes to the app. Then you should turn on the screen reader and try the same tasks while using the screen reader. Finally, run the accessibility scanner on each of the screens.
You will need to use a combination of XML modifications and modifications to the source code to make AskforHelp accessible. We have put TODOs in the code where our solution required code changes.
Some stylistic rules to keep in mind
- For any repairs involving new strings, you must add a new entry for the fix into the
strings.xmlfile, and then reference it elsewhere in the code. - For any repairs involving numbers, you must modify (or add to) the
dimens.xmlfile. - For any repairs involving colors, you must modify (or add to) the
colors.xmlfile.
You may change the wording in an entry in strings.xml or values in dimens.xml or colors.xml but you must not remove any entries from the original files.
Recall that reference values in any of these by specifying @<filename>/<valuename>.
4. Write your reflection.
You will answer the following questions using the format provided in Gradescope.
- Give an example of a problem that was not solved simply by writing good alt text. Tell us
- How you identified that problem
- How you fixed the problem
- Whether Android’s accessibility tools were helpful in identifying or fixing it
- AskforHelp requires the user to interact with standard android apps (contacts and messaging). Try to do this with the screen reader and tell us about any accessibility issues you found .
- Provide a list of the alt text strings that you wrote
5. Make a video
Make a video of yourself completing all four tasks, in order, using the screen reader. As a reminder these tasks are:
- Go to settings from the home screen and turn on location
- Add a request
- Choose a request, choose a contact, and send the request
- Delete a request
When doing these tasks, you should demonstrate navigation order by swiping from item to item, rather than using your eyes or knowledge of location on screen to complete them.
You can achieve the recording in many ways, however the easiest may be to start a Zoom meeting and press the
record button, then hold up your physical phone to show how you are testing. Record the session to your computer which will result in a .mp4 when you exit the Zoom
meeting. See below for instructions on how to turn in the .mp4 file.
Turn-in
Submission Instructions
You will turn in your code via GitGrade. The files you will need to include are:
- dimens.xml
- strings.xml
- colors.xml
- any other xml files you need to change to improve accessibility
- any .java files you need to change to improve accessibility
Grading (40pts)
Tentative rubric:
Grading of video (14 total):
- 4 pts Video has all the required components
- 2 pts Navigation efficiency when swiping
- 2 pts Low-vision accessibility concerns addressed
- 2 pts Motor accessibility concerns addressed
- 4 pts Other factors that improve accessibility
Grading of code (14 total):
- 2 pts Use of XML files demonstrates minimal redundancy
- 2 pts Colors meet standards specified in Make apps more accessible
- 2 pts Dimensions meet standards Make apps more accessible
- 2 pts All UI elements needing descriptions are described
- 2 pts UI element descriptions are in strings.xml
- 2 pts Code follows best practices for Editable elements described in Principles for improving app accessibility
- 2 pts Code includes proper accessibility announcements when something on screen changes
Grading of reflection (12 total):
- 4 pts Reflection on a problem not solved by Alt text
- 4 pts Reflection on accessibility of standard android apps.
- 4 pts Quality of alt text (excess or insufficient alt text will both lose points) per Webaim’s guidelines and those in Make apps more accessible