Discuss
While you're settling in, discuss with someone near you...
-
What did you notice in the
about.htmlfile that you would like to know more about? - How did it go for you in section yesterday? What did you learn in getting your machine set up and accepting CP1?
- What was the icebreaker you did in section and what were the results of the icebreaker discussions?
CSE 154
Lecture 2: More HTML, Accessible design
Today's Agenda
Administrivia
Discuss Accessible Design
Finish discussing HTML
Yes really!
but you should not feel like you will know everything yet
and we do learn more as we delve deeper into CSS and JS
Start CSS
But first...
Should you take this course?!?!?
Answer yes if...
- You are really curious about how web sites work
- You are ready to learn several different languages and technologies within a 10-week quarter with structure, resources, and support of a CSE course (as opposed to resource-overload on the web)
- You want to learn a bit about the human connection to web development
Answer no if...
- You are not willing too put in the effort befitting of a rigourous 5 credit course in computer science.
- You do not plan to come to sections, use course read the course materials, or use other resources that are available to help you succeed
- You only want to use this course as a way "get into CSE"
Administrivia
WPL starts today after class (SIG 228)
Sections
- Sections will reinforce learning from lectures
- Quick checks in Tuesday section starting next week
- Attend the section you are signed up for!
Atom with Git (and cloning!)
- Atom/Git Set Up guides updated (which can be found here) to include git clone using ssh instead of https
- Do not change anything you have already set up for CP 1
- Our lab staff would prefer if we use ssh
Think-Pair-Share
What website would you build if you already knew "enough" about web programming?

Assignments
Creative Project 1
Due: Saturday, April 6, 11:00 pm
GitGrade Lock: April 7, 11:00 pm
Homework 1
Due: Thursday, April 11, 11:00 pm
GitGrade Lock: Sunday April 14, 11:00 pm
Also a reminder to sign up for Mentor Circles by Friday! (but the sooner the better)
Review: Internet
Things that are relevant
- There are layers
- IP = Internet Protocol, addresses like 192.168.0.1
- No centralized control but...
- DNS maps the numbers to names like Google.com
- W3C Validates web pages
- Websites use a client-server model over the Internet
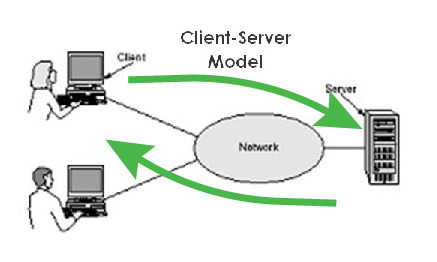
From Wikipedia
Review: Websites
Content

Words and images
Structure
HTML
Style

CSS
Behavior
Javascript & Server programs

HTML
Hypertext Markup Language (HTML)
Describes the content and structure of information on a web page
- Not the same as the presentation (appearance on screen)
Surrounds text content with opening and closing tags
Each tag's name is called an element
- Syntax:
<element> content </element> - Example:
<p>This is a paragraph</p>
Most whitespace is insignificant in HTML (ignored or collapsed to a single space)
We will use a newer version called HTML5
Structure of an HTML Page
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
information about the page
</head>
<body>
page contents
</body>
</html>HTML
The <head> tag describes the page and the <body> tag contains the page's content
An HTML page is saved into a file ending with extension .html
The DOCTYPE tag tells the browser to interpret our page's code as HTML5, the lastest/greatest version of the language
HTML Tags
There are many different types of HTML tags used to structure web pages (we can't possibly cover all of them within lecture).
A comprehensive list is here (it's a great bookmark page for reference this quarter!)
Unless otherwise specified, all of the tags listed are required to be in the <body> of an HTML page rather than the <head>
Our compiled list is here and here
A few details
- HTML is a subset of Extensible Markup Language (XML) (more info)
- Tags that start with
<!like is<!DOCTYPE html>is considered Markup Declaration -
Self-closing tags like Horizontal Rule
<hr>can either have the slash in the tag or not, but BE CONSISTENT IN YOUR CODE.
<hr />
<hr>Two (equivalent) examples of the self-closing horizontal rule tag (HTML)
Q: The img tag is another self-closing tag. What characteristics do these two tags have that make them appropriate as "self-closing" compared to content-holding tags like the paragraph tag?
HTML vs Rendered Web Page
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>About Me: Nicole Riley</title>
</head>
<body>
<header>
<h1>About Me: Nicole Riley</h1>
</header>
<main>
<article>
<p>Hello, everyone! My name is ......</p>
</article>
</main>
...
</body>
</html>
Attributes
Some tags can contain additional information called attributes
- Syntax:
<element attribute="value" attribute="value"> content </element> - Example:
<a href="page2.html">Next page</a>
Where else did you see attributes yesterday?
<html lang="en">
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<img src="" alt="insert descriptive text for screenreaders" />
<img src="" alt="insert descriptive text for screenreaders" />
Accessible Design
Slides based on content from Profs. Richard Ladner, Jake Wobbrock, and Amy Ko.
Disabilities
Everyone has different abilities
Nearly 1 in 5 people have a disability in the U.S. (from the U.S. Census)
(Some) kinds of disabilities
from W3C Web Accessiblity Initiative (WAI)
- Visual
- Blind
- Low-Vision
- Color Blind
- Auditory
- Deaf
- Hard of Hearing
- Speech
- Ability to speak
- Speech impediments
- Physical
- Ability to Walk
- Ability to use limbs
- Cognitive, learning, and neurological
- Dyslexia, dysgraphia, dyscalculia
- ADHD
- Memory loss
- Learning disabilities
- Behavioral
- Bipolar
Temporary and Situational Disability
Disabilties can be temporary
- having a broken arm in a cast
- difficulty hearing after a loud concert
Disabilties can be situational
- trying to open your door while carrying groceries
- trying to talk on the phone in a noisy room
- trying to read your phone under direct sunlight
Disability affects all of us
Accessible Design
Designs that account for all abilities are called accessible designs
Try your phone's screen reader!
Enable your phone's screen reader
- iOS: Settings > General > Accessibility > VoiceOver > Hit the switch
- Android: Settings > Accessibility > Talkback > Hit the switch
Input works differently now. For example, tap now reads the screen and double-tap selects. Use two or three fingers to scroll by page. Play with it for a minute.
Try closing your eyes and reading a webpage or a social networking site. Try writing an email.
Views of disabilities
Medical view
- Disabled people are patients who need treatment and/or cure.
Legal view
- Disabled people have rights and responsibilities, such as access to public buildings, voting, education, etc.
- Lawsuits can occur, but they should not be the motivating factor for making a system accessible
Sociocultural view
- Variation in ability is natural. "Disability" is caused by how society is designed, not by nature.
- Building for inclusion builds innovation (e.g., curb cuts, close captioning)
Universal Design
Design for as many users as possible, not just the average user
Example: Airplane cockpits:
- In 1952, the U.S. Air Force redesigned seats to fit the average pilot.
- They fit nobody (nobody is actually average), training results dropped.
- Redesigned seat to be configurable for any pilot; training results rose above previous levels.
Universal Design is often used in architecture
Universal Design Principles
- Equitable use
- Flexibilty in use
- Simple and intuitive
- Perceptible information
- Tolerance for error
- Low physical effort
- Size and space for approach and use
Ability Based Design
Instead of focusing on the abilities that someone lacks (dis-ability), and trying to compensate
Focus on making systems work with what abilities people have
Don't make people adapt to the system 
Make the system adapt to the abilities of the user
Ability Based Design Principles
- Focus on Ability, not dis-ability.
- Accountability: If user has difficulty, system changes.
- Adaptation: Interface may be self-adaptive or user-adaptable.
- Transparency: Give user awareness of adaptations
- Performance: System may monitor users' performance
- Context: System may sense context
- Commodity: System may be affordable
First two are required, other five are recommended
Tools and Resources
From the A11y Project
- A really great compendium of resources
- An accessibility workshop from GHC'18
Tools
- Web Accessability Evaluation Tool: http://wave.webaim.org/
- Color Schemes: http://colorbrewer2.org/
- Color blindness checker: http://www.color-blindness.com/coblis-color-blindness-simulator/
- Text readability: http://juicystudio.com/services/readability.php
Resources
- Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (something to know about when you apply for jobs): https://www.w3.org/WAI/intro/wcag
- Teach Access Tutorial (general background and covers an important standard called ARIA). http://teachaccess.org/initiatives/tutorial/
- Web design and development course by AccessComputing http://www.washington.edu/accesscomputing/webd2/
- A11ycast - YouTube Videos to teach developers how accessibility works.
Back to HTML
Semantic Tags
Discuss
What did you learn from the readings?
- Name some of the HTML5 semantic tags
- Why would we want to use a semantic tag for structuring our HTML document?
- Did you see any semantic tags in your aboutme.html?
- Did you see anything in your aboutme.html that would help make your site accessible?
article vs section
We get this question a LOT
Others ask this too
Here are two resources to help you:
- Ian Devlin article (a course reading)
- Youtube video
Basically: Article should be standalone content. Section is not.
And remember: div div has no semantic meaning,
should only be added for selecting content in CSS/JS, and should be your "last resort"
Accessible Web Design Principles
- Use document structure (Semantic) tags: e.g.,
<article>,<strong> - Don't use deprecated style tags like
<b> - Provide metadata: e.g.,
<html lang="en"> - Provide alternatives: e.g., img alt tag, video captions, transcripts, allow both keyboard and mouse input
- Avoid directional text: eg. "the diagram on the right shows..."
Note: These design principles help in other ways as well
- Captions allow people to watch your video without turning sound on.
- Transcripts help people find your page through Google.
- Structure and metadata help programs understand your page.
Use alt attributes on images
<img src="img/koalafications.jpg" alt="Koalified koala" />HTML

output
The src attribute specifies the image URL
HTML5 also requires an alt attribute describing the image, which
improves the web page
experience for all (if the image doesn't load)
Images and Links
<a href="http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Koala/">
<img src="images/irrelephant.jpg" alt="Irrelephant elephant"
title="dumbo!" />
</a>HTML
What's the title attribute?
-
titleattribute is an optional tooltip (on ANY element) -
BUT the
titleattribute doesn't always work well for mobile and accessibility, so its usage and future are debated
A note about images that are links
White space usually doesn't matter in HTML pages, except apparently here
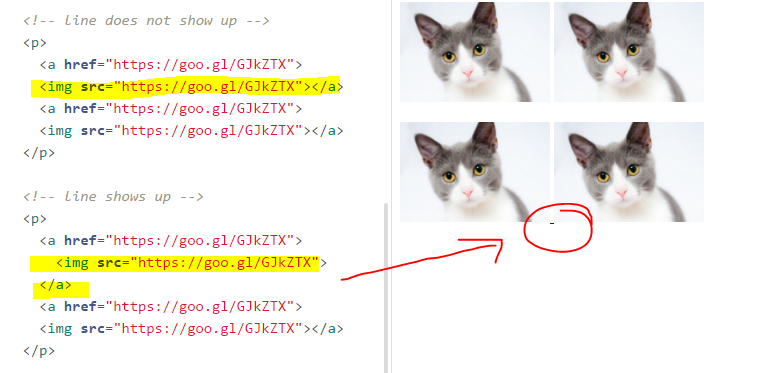
Preview of imagelinktext.html
Review: Websites
Content

Words and images
Structure

HTML
Style

CSS
Behavior

Javascript & Server programs

CSS (preview)
The Bad Way to Produce Styles
<p>
<font face="Arial">Welcome to Greasy Joe's.</font>
You will <b>never</b>, <i>ever</i>, <u>EVER</u> beat
<font size="+4" color="red">OUR</font> prices!
</p>
HTML
Welcome to Greasy Joe's. You will never, ever, EVER beat OUR prices!
output
Tags such as b, i, u and font are discouraged in strict HTML
Why is this bad?
- Accessibility
- Code organization
- Changing style easily
Cascading Style Sheets (CSS): <link>
<head>
...
<link href="filename" rel="stylesheet" />
...
</head>HTML (template)
<link href="style.css" rel="stylesheet" />HTML (example)
CSS describes the appearance and layout of information on a web page (as opposed to HTML, which describes the content)
Can be embedded in HTML or placed into separate .css
file (preferred)
Basic CSS Rule Syntax
selector {
property: value;
property: value;
...
property: value;
}CSS (template)
p {
color: red;
font-family: sans-serif;
} CSS (example)
A CSS file consists of one or more rules
A rule selector specifies HTML element(s) and applies style properties
- A selector of
*selects all elements
