name: inverse layout: true class: center, middle, inverse --- # The Whole Toolkit Part I ## Input Lauren Bricker CSE 340 Spring 23 --- layout:false [//]: # (Outline Slide) # Goals - **Get input from the user** (part 1) - Produce output for the user (part 2) - How to store application specific data (part 3) --- # The Whole Toolkit Architecture .left-column50[ - Input - (C/M?) Input models (events) - (C/M?) Event dispatch - (C/M?) handling (state machine) - (C/M?) Callbacks to application - Output - (V) Interactor Hierarchy design & use - (V)Drawing models (`onDraw()`) - (V)Layout (`onLayout()` or `XML`) - (V) Damage and redraw process ] .right-column50[ - End User - Input: The user does actions with the mouse, keyboard and other peripherals. - Output: Changes views on the screen, to audio, etc. - App Developer - Input: writes callbacks - Output: may call `invalidate()` - Component Developer - Input: needs to understand everything we talked about - Output: needs to understand everything we talked about ] --- # The Whole Toolkit Architecture - Input - **Input models (events)** [more info](/courses/cse340/23sp/slides/wk04/events.html#27) - Event dispatch - Event handling (state machine) - Callbacks to application - Output - Interactor Hierarchy design & use - Drawing models (`onDraw()`) - Layout (`onLayout()` or `XML`) - Damage and redraw process - Storage - Bundles - Shared Preferences --- # Events An event is a representation of user input - Lots of types of devices (sound, finger, mouse, light) - We need device independence - To handle a variety of ways to get input (finger, mouse, etc) - We need a uniform and higher level abstraction for input (events) - Device differences - Handled implicitly by only creating events they can generate - Types of events - Discrete events (e.g. mouse or key click, "when" something happens) - Sampled devices - Handled as “incremental change” events - Each measurable change: a new event with new value --- # Contents of Event Record What do we need to know about each UI event? **What**: Event Type (mouse moved, key down, etc) **Where**: Event Target (the input component) **When**: Timestamp (when did event occur) **Value**: Mouse coordinates; which key; etc. **Context**: Modifiers (Ctrl, Shift, Alt, etc); Number of clicks; etc. ??? Discuss each with examples --- # Events Which of the following does NOT generate an event? A. Pressing the ALT key <br> B. Pressing the K key <br> C. Pressing your finger on the phone screen <br> D. Moving a mouse across the screen (on a computer) -- ALT does not generate an event (it is a modifier) Everything else does --- layout:false # The Whole Toolkit Architecture - Input - Input models (events) - **Event dispatch** more info [here](/courses/cse340/23sp/slides/wk05/event-delivery.html#25) and [here](/courses/cse340/23sp/slides/wk05/pps-geom.html#5) - Event handling (state machine) - Callbacks to application - Output - Interactor Hierarchy design & use - Drawing models (`onDraw()`) - Layout (`onLayout()` or `XML`) - Damage and redraw process - Storage - Bundles - Shared Preferences --- # Event Dispatch: Picking .left-column40[ <div class="mermaid"> graph TD A[0: Drawing Canvas] --> B(1: CircleA, Green) A --> C(2: LineB, Orange) B --> D(3: LineA, Black) C --> E(4: PointA, Blue) C --> F(5: PointB, Black) </div>  ] .right-column60[ An interactor hierarchy and the corresponding interface are shown to the left. If the user clicks on the image at (4,4) what will be the order of views in the filtered pick list? Assume that the drawing canvas does not accept touch input. ] ??? - 3: LineA (Black) - 1: CircleA (Green) Nothing else is positionally associated --- # Event Dispatch: Picking .left-column40[ <div class="mermaid"> graph TD A[0: Drawing Canvas] --> B(1: CircleA, Green) A --> C(2: LineB, Orange) B --> D(3: LineA, Black) C --> E(4: PointA, Blue) C --> F(5: PointB, Black) </div>  ] .right-column60[ An interactor hierarchy and the corresponding interface are shown to the left. If the user clicks on the image at (4,4) what will be the order of views in the filtered pick list? Assume that the drawing canvas does not accept touch input. - 3: LineA (Black) - 1: CircleA (Green) Nothing else is positionally associated ] --- # Event Dispatch: Delivering Review - Top-down, Bottom-Up, Bubble-out, Focused-based: these are theoretical Event dispatch approaches. - *Capture* is rarely used by component developers - Capture is top-down: start on the in the biggest interactor that contains the event, then narrow in on which window actually will use the event - *Bubbling* is far more common - Bubbling is bottom-up - start with the window at the front (the last drawn, lowest in the interactor tree) - see if the event is consumed by that interactor. If not, go up the tree. - Android does it a bit differently. - Hacky version of picking and filtering - Most stuff is in bubble order, but some callbacks assume you consume the event (no option to return `true` vs `false`) --- # Event Dispatch: Bubble .left-column40[  ] .right-column60[ For the same image, what interactor will get the event first in Bubble? ] -- .right-column60[ LineA, Black <br> ] -- .right-column60[ Because it is the last thing (under the locator event) drawn (reflected in its position in the interactor hierarchy) ] --- # Focus versus Positional dispatch In which of the following situations is focus dispatch used during event handling, and in which is positional dispatch used? - When a key is typed? - When a button is clicked? - When a user swipes on the screen? - When doing rubberbanding of a line (click, drag, release) --- layout:false # The Whole Toolkit Architecture - Input - Input models (events) - Event dispatch - **Event handling (state machine)** [more info](/courses/cse340/23sp/slides/wk05/pps-geom.html#39) - Callbacks to application - Output - Interactor Hierarchy design & use - Drawing models (`onDraw()`) - Layout (`onLayout()` or `XML`) - Damage and redraw process - Storage - Bundles - Shared Preferences --- # Essential Geometry represents places .left-column-half[  ] .right-column-half[ - Example: The essence (or nature) of this scrollbar/where can you interact with it is: - on the thumb - inside the scrollbar above the thumb - inside the scrollbar below the thumb ] --- # PPS uses Essential Geometry .left-column40[ Button <div class="mermaid"> stateDiagram-v2 [*] --> INSIDE: DOWN / indentButton() INSIDE --> OUTSIDE: MOVE / <BR> Outside ? normalButton() OUTSIDE --> [*]: UP / cancelAction() INSIDE --> [*]: UP / invokeAction() OUTSIDE --> INSIDE: MOVE / <BR> Inside ? indentButton() </div> ] .right-column60[ Scrollbar <div class="mermaid"> stateDiagram-v2 [*] --> Scrolling: MouseDown / Inside [*] --> Ready: MouseMove / Inside Ready --> [*]: MouseClick / <BR> AboveThumb?<BR>Scrollup() Ready --> [*]: MouseClick / <BR> BelowThumb?<BR>Scrolldown() Ready --> [*]: MouseMove / <BR> Outside Scrolling --> Scrolling: MouseMove / <BR> UpdateThumbDocument() Scrolling --> [*]: MouseUp / <BR> KeepLocation() </div> ] Then from the PPS you can generate the code for this interactor. --- # Like Button Example .left-column[ <br> 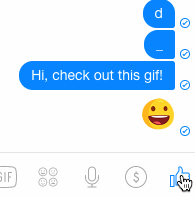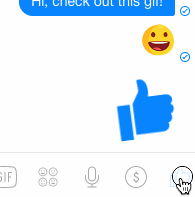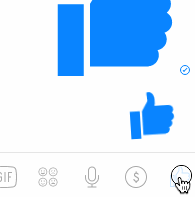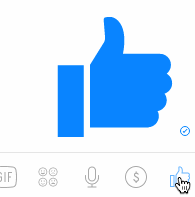 ] .right-column[ - Determine the Events (triggers) - Determine the States - Determine the Queries (essential geometry, context) - Determine the Actions ] ??? What constitutes an “event” varies - may be just low level events, or - higher level (synthesized) events - e.g. region-enter, press-inside What is missing? Query fields --- # Like Button Example .left-column[ <br>  ] .right-column[ - Determine the Events (triggers) - MouseDown, MouseUp, MouseMove - Determine the States - PRESS/NOT_PRESSED - Determine the Queries (essential geometry, context) - INSIDE/OUTSIDE - Determine the Actions - highlight()/unhighlight(), startAnimation(), updateAnimation(), finishAnimation(), addToChat() ] --- # Like Button Example .left-column[ <br>  ] .right-column[ <div class="mermaid"> stateDiagram-v2 [*] -->PRESSED: MouseDown/INSIDE? highlight(),startAnimation() PRESSED --> PRESSED: updateAnimation() PRESSED --> PRESSED: finishAnimation(), !small PRESSED --> [*]: MouseUp/INSIDE/small? unhighlight() PRESSED --> [*]: MouseUp,INSIDE/!small,addToChat(),unhighlight() </div> Note : This does not include the states if the mouse moves off the button while still the user still has the mouse button pressed. ] --- # Reminders: - PPSs are good for helping you to design your interactions/interactors - PPSs are a good way to do control flow in event driven systems - You can use PPSs to do (formal or informal) analysis - are all possible inputs (e.g. errors) handled from each state - what are next legal inputs: can use to enable / disable - PPSs can be automated based on higher level specification --- layout:false # The Whole Toolkit Architecture - Input - Input models (events) - Event dispatch - Event handling (state machine) - **Callbacks to application** [more info](/courses/cse340/23sp/slides/wk05/event-handling.html#11) - Output - Interactor Hierarchy design & use - Drawing models (`onDraw()`) - Layout (`onLayout()` or `XML`) - Damage and redraw process - Storage - Bundles - Shared Preferences --- # Callbacks in Android - At the time Android was created the toolkit developers have *no* idea how every app may want to respond to events - Listeners are an interface that acts as a _callback_ method - Recall interfaces specify behavior (but no data) that can be inherited. - Must be *registered with* a particular `View` - The toolkit architecture (implemented in `View`) then delivers events that arrive at *that View* to *those listeners* - i.e. once the `View` is interacted with by the user - A `View` can have listen for different types of interactions --- # Standard Listener Interfaces The toolkit has pre-defined interfaces so apps or components can respond to events such as clicks or touches. ```java // User tapped a view public static interface View.OnClickListener { ... } // User long pressed on a View public static interface View.OnLongClickListener { ... } // State of view has changed // (e.g. user clicked outside a EditText input box) public static interface View.OnFocusChangeListener { ... } // user typed something public static interface View.OnKeyListener { ... } ``` --- # Different types of callbacks .left-column40[ 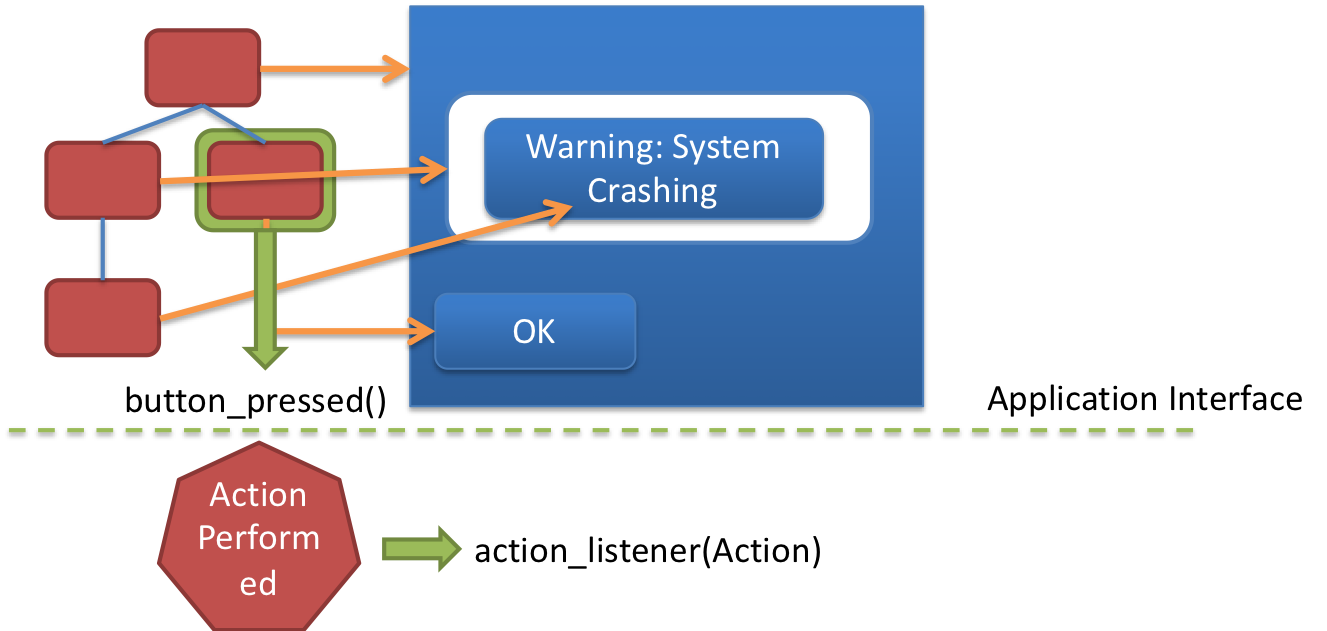 ] .right-column60[ Some callbacks are - registered with the system (`onCreate`, `onResume`, ...) - triggered by a timer. - triggered by our Measure (onMeasure), Layout (onLayout), Invalidate (onDraw) And ... - created by the Component Developer! (i.e. onColorSelected) ] --- # Review: Model View Controller (MVC) .left-column60[ <div class="mermaid"> sequenceDiagram loop Every time user provides input Note right of View: User provides input View->>Controller: Input Controller->>Model: Change state Model->>Controller: Update state of View(s) Controller->>View: Triggers redraw Note right of View: User sees response end </div> ] .right-column40[ **Goal:** separation of the view from the underlying model (data) ] --- # Custom Callback Example (ColorPicker) .left-column60[ <div class="mermaid"> sequenceDiagram participant Application participant AbstractColorPickerView participant User Application->>AbstractColorPickerView: addColorChangeListener(this) User->>AbstractColorPickerView: Interacts with color picker AbstractColorPickerView-->>Application: onColorSelected() </div> ] .right-column40[ <div class="mermaid"> classDiagram class ColorChangeListener { } class AbstractColorPickerView{ #mColorChangeListeners +addColorChangeListener() +removeColorChangeListener() +invokeColorChangeListeners() } class Application { onColorSelected() } ColorChangeListener <|-- Application : Implements AbstractColorPickerView --> "many" ColorChangeListener : Contains </div> ] --- # End of Part I