name: inverse layout: true class: center, middle, inverse --- # Analyzing Quantitative Data Lauren Bricker CSE 340 Spring 23 --- layout:false [//]: # (Outline Slide) # Today's Agenda - Administrivia - Thank you to Thevina for covering for me! - If you can't complete Menus with your custom menu by Fri 5-May, reach out on [Ed](https://edstem.org/us/courses/38124/discussion/) and we'll send you an `.apk` that you can load and test with. - Questions on [Menus experiment design](menus-experiment.html) - Analyzing data - Dependent and independent variables - Discuss how we determine causality - Practice onboarding participants - Practice data analysis --- # Reminder on [Academic Conduct](/courses/cse340/23sp/#academic-conduct) - You are expected to turn in your own [work that demonstrates your understanding](/courses/cse340/23sp/academic-conduct.html#collaboration-policies) - You **may not** copy your code or reflection answers directly from another student or any other source on the internet. - You may not use/copy any part of your course work from **AI-assistance such as GitHub Copilot, ChatGPT, etc.** - You will be asked, in each reflection, to acknowledge any help you received from another person or internet resource. Additionally it is always good practice to also cite your sources with a comment in your code as well. - Students are expected not to share code/solutions with the broader public, and not to plagiarize or cheat, as described in the [Allen school conduct guidelines](https://www.cs.washington.edu/academics/misconduct). --- name: inverse layout: true class: center, middle, inverse --- # Determining Causality ## thinking theoretically... --- layout:false # Dependence/independence Events that are independent - Flipping heads and then tails - Day of week and whether a patient had a heart attack (probably?) Events that are dependent - Vice presidential candidate and presidential nominee - Diagnostic test being positive and whether patient has a disease -- What are some dependent and indepenent relationships in the Menus study? ??? Think about a coin flip: one flip does not depend on another. What if we collect this kind of data, what might be true about it? --- # What might we expect to see is true of dependent variables? - When one changes, the other changes at the same rate - When one changes, the other changes at a faster rate - When one changes, the other does the opposite ??? Called a correlation We can see it in a scatter plot Go look at data and make one --- # This is called *Correlation* We can see it in a *scatterplot*  --- # Correlation (active) Demo Active demo: * Open it yourself: [https://tinyurl.com/cse340-23sp-tts-data](https://tinyurl.com/cse340-23sp-tts-data) * Make a copy of this sheet to your own drive using File->Make a copy. (You must be logged into a Google account to make a copy) Data courtesy of Deepti Ramani from a CSE 163 assignment * Base on the [Tiktok API](https://developers.tiktok.com/doc/tiktok-api-v2-video-object/) and [Spotify API](https://developer.spotify.com/documentation/web-api/reference/#/operations/get-several-audio-features) * Data gathered monthly from Jan 20 - Mar 21 * The rank is the ranking (top 100) of the audio on TikTok for that month * No Spotify data for many songs. ??? [OpenSecrets.org data set on internet privacy resolution](https://www.opensecrets.org/featured-datasets/5) Older demo: [tinyurl.com/cse340-22sp-ip-data](https://tinyurl.com/cse340-22sp-ip-data) --- # Correlation demo [TikTok vs Spotify data set](https://tinyurl.com/cse340-23sp-tts-data) - Select two columns (use command/control click to select 2 columns) - Use Insert->Chart - Make sure this is a scatterplot --  Is there a correllation? ??? Older demo: [tinyurl.com/cse340-22sp-ip-data](https://tinyurl.com/cse340-22sp-ip-data) --- # Correlation != Causation  --- # Correlation != Causation  .footnote[[XKCD](https://xkcd.com/552/)] --- # Filtering for analysis Select **column B**, then select **Data->Create A Filter**. Click on the newly shown green downward facing triangle, then select a month (like June 2020). This filters so that only the data from June 2020 is shown. Create a Rank vs Views and Videos chart with this filtered data (columns E, G, I) -- count: false .left-column60[ It might be helpful for this chart to use a log scale for the vertical axis. In the chart editor, select the **Customize** tab, then open up the **Vertical Axis**. Toggle the **Log Scale** checkbox. ] .right-column40[  ] --- # Grouping for analysis .left-column60[ [TikTok vs Spotify data set](https://tinyurl.com/cse340-23sp-tts-data) Pivot Tables can help to sort out a lot of data. Example * Select **Insert->Pivot Table** and make it go on a new sheet * Values: add Number of TikTok Views, and Number of TikTok Videos * try changing from Sum to Average * Chart the resulting table * Try changing to a line chart (use the hamburger menu on the chart to edit the chart) ] -- count: false .right-column40[  ] ??? Old data  --- # Grouping and charting What do you see in the difference between tasks on each of these menus types?  -- count: false Charting gives you a place to start, what questions you might want to ask. --- # Grouping and charting helps you check your assumptions [23sp Sample data](https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1OzrfHU3WAKbBBfucCb2xQlU8JL9tZcrSybWvQQEMoQ0/edit?usp=share_link) **Notes** - this is based off only one person doing all three sessions. - You likely will get better results with your data because you're doing 3+ distinct users - We will get even better results with ALL of the data merged together - (Remember to turn your CSV into the Canvas Assignment so we can combine) --- # Data Collection .left-column[  ] .right-column[ Click on the **Example Chart** tab. Here you can - Analyze and chart data: Simple Statistics - Min, Max, Mean (Sum/#), Median (Middle #), Mode (Most Common #) Demo Do this for speed *and* error. ] --- # Comparing groups to see if they are different Bar charts are not enough to assess difference though. Need to see the *distribution* A distribution is looking at how the people we are studying distributed over a specific variable we care about. A histogram graphically shows a distribution. --- # Histogram shows you a *distribution* [TikTok vs Spotify data set](https://tinyurl.com/cse340-23sp-tts-data) .left-column40[ Pivot table * Rows are TikTok rank * Values are * Acousticness * Dancability * Energy * (pick your own!) Select Histogram ] .right-column60[  ] ??? Old data  --- # But having the right chart matters  --- # Normal Vs Pie |Normal | Pie| |--|--| ||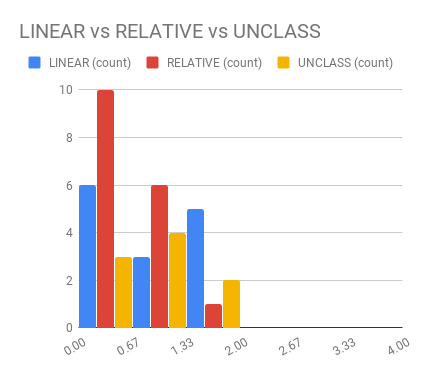| The cause of the difference only shows here. --- # What do we learn from a histogram? 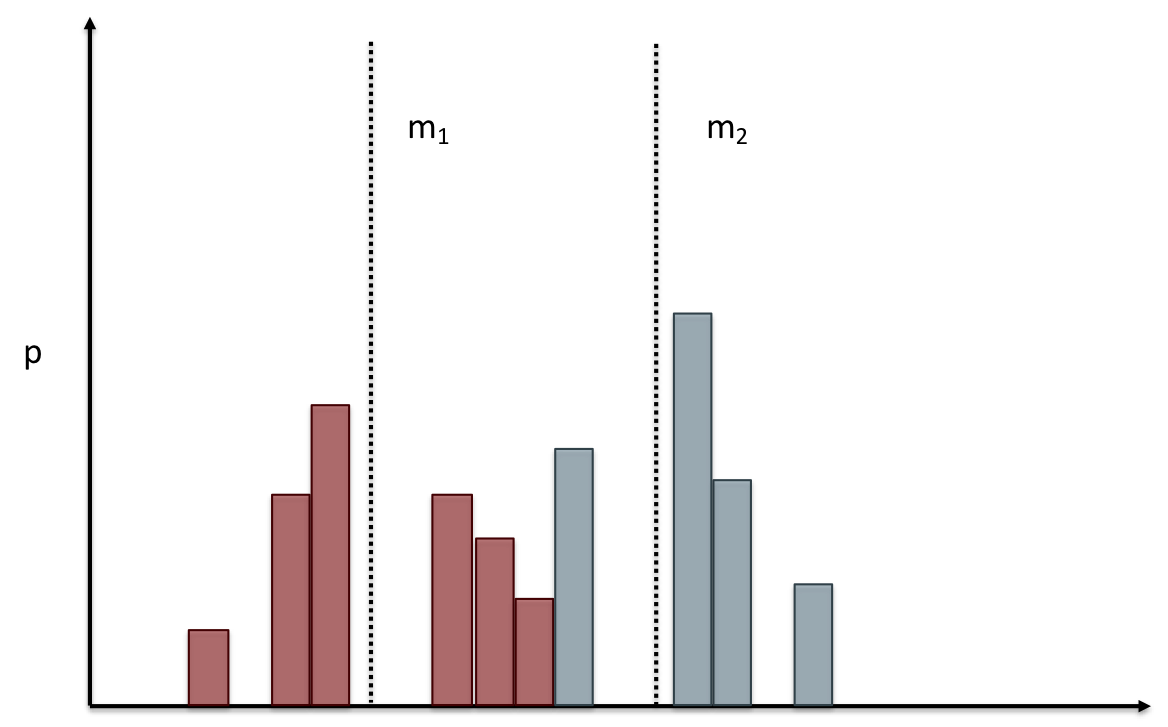 ??? - shows a distribution - helps us tell if things are INDEPENDENT --- # Histograms What do we learn from a histogram? - shows a distribution - helps us tell if things are INDEPENDENT --- # Comparing two groups 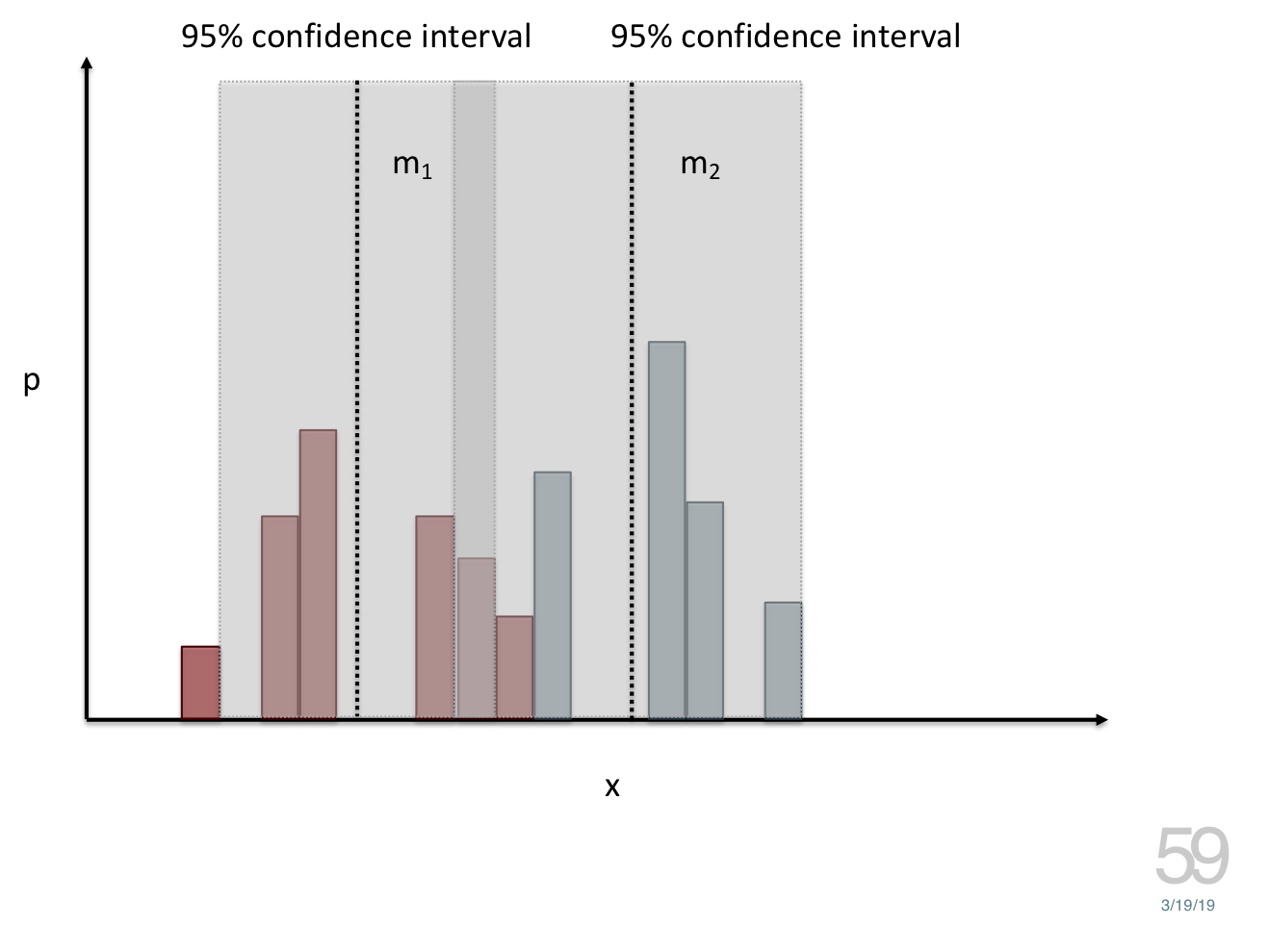 --- # Comparing two groups 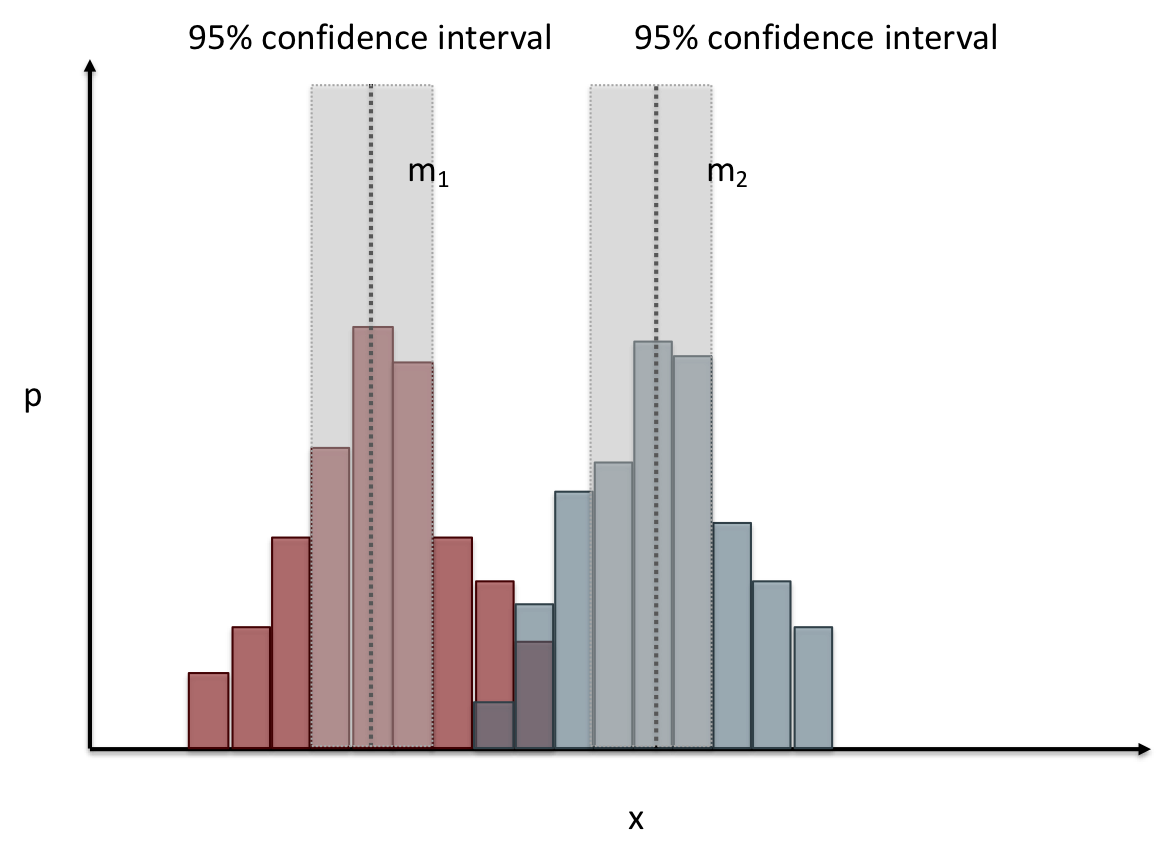 --- # Comparing two groups 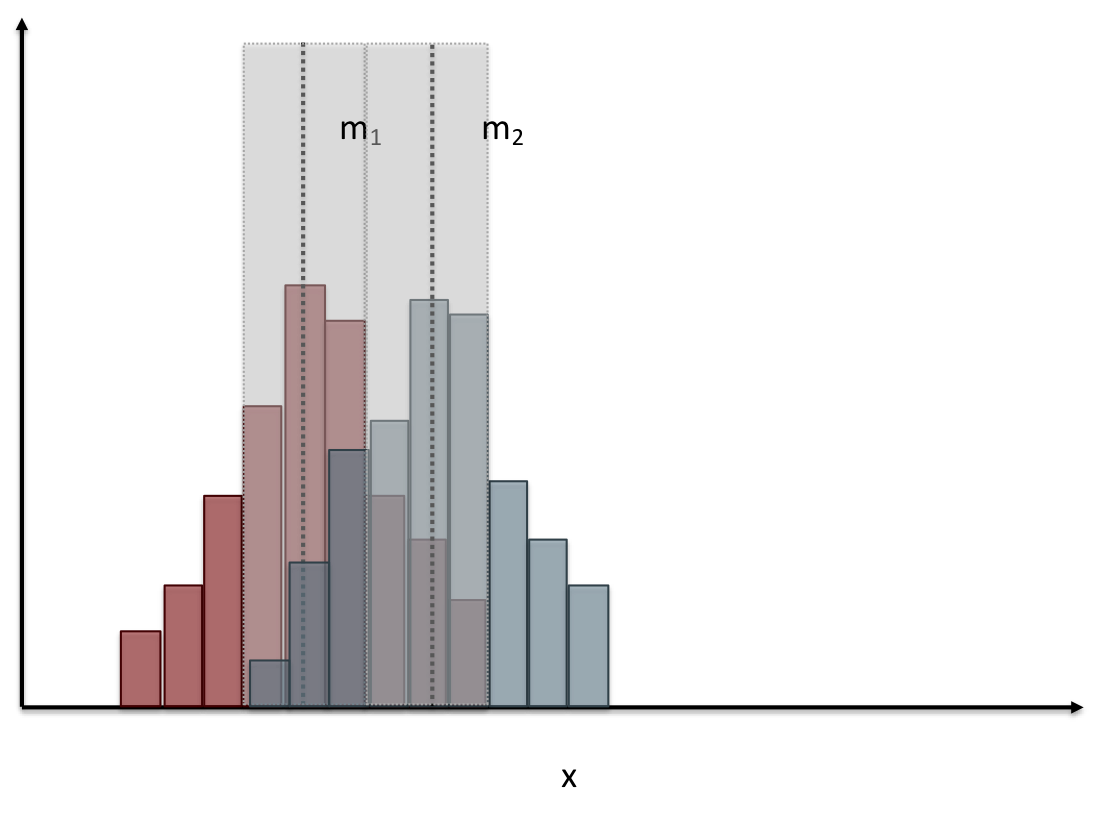 --- # Comparing two groups 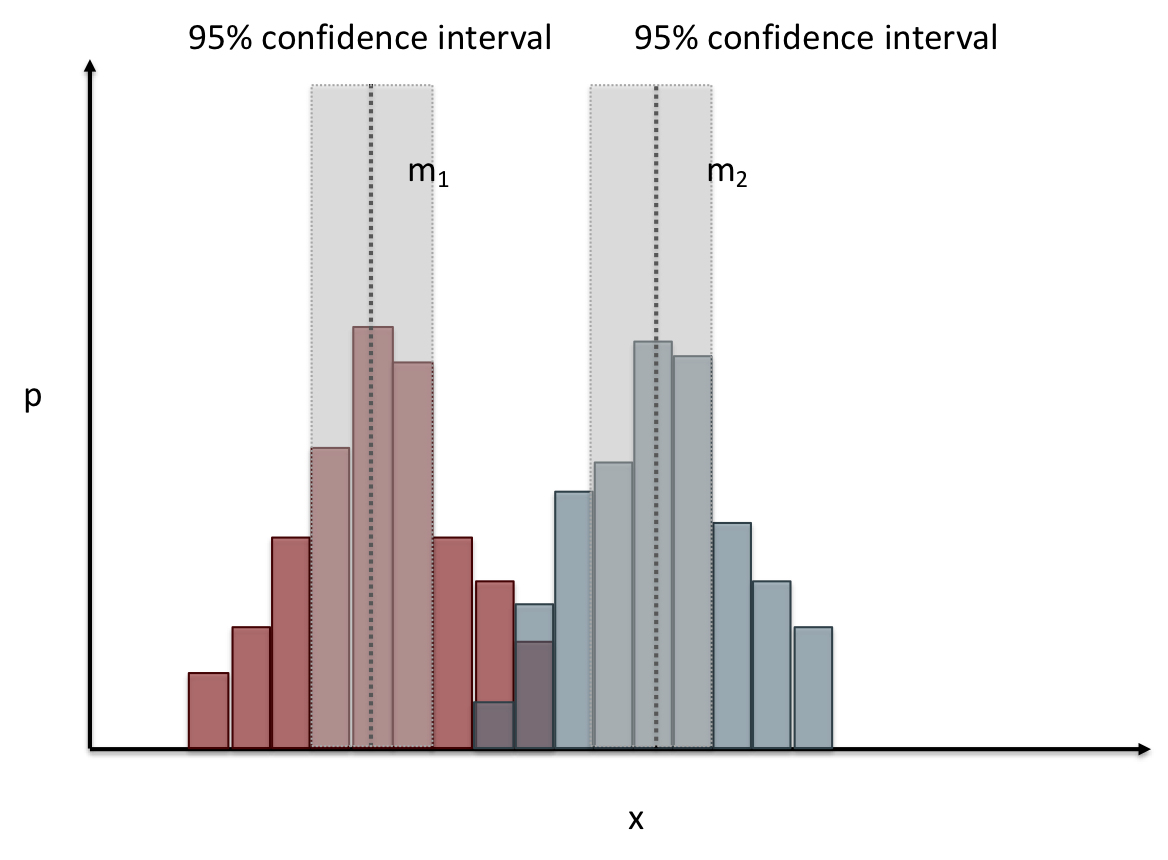 --- # Comparing two groups 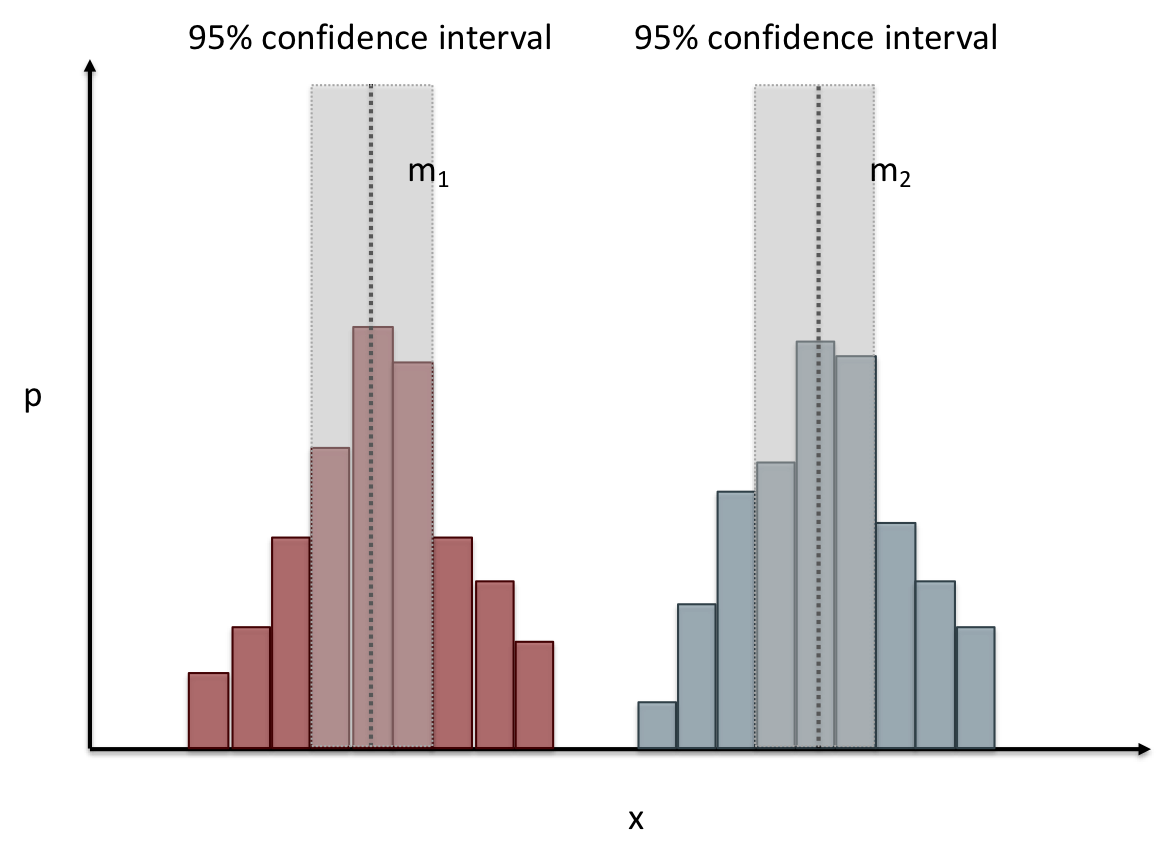 --- # Comparing two groups 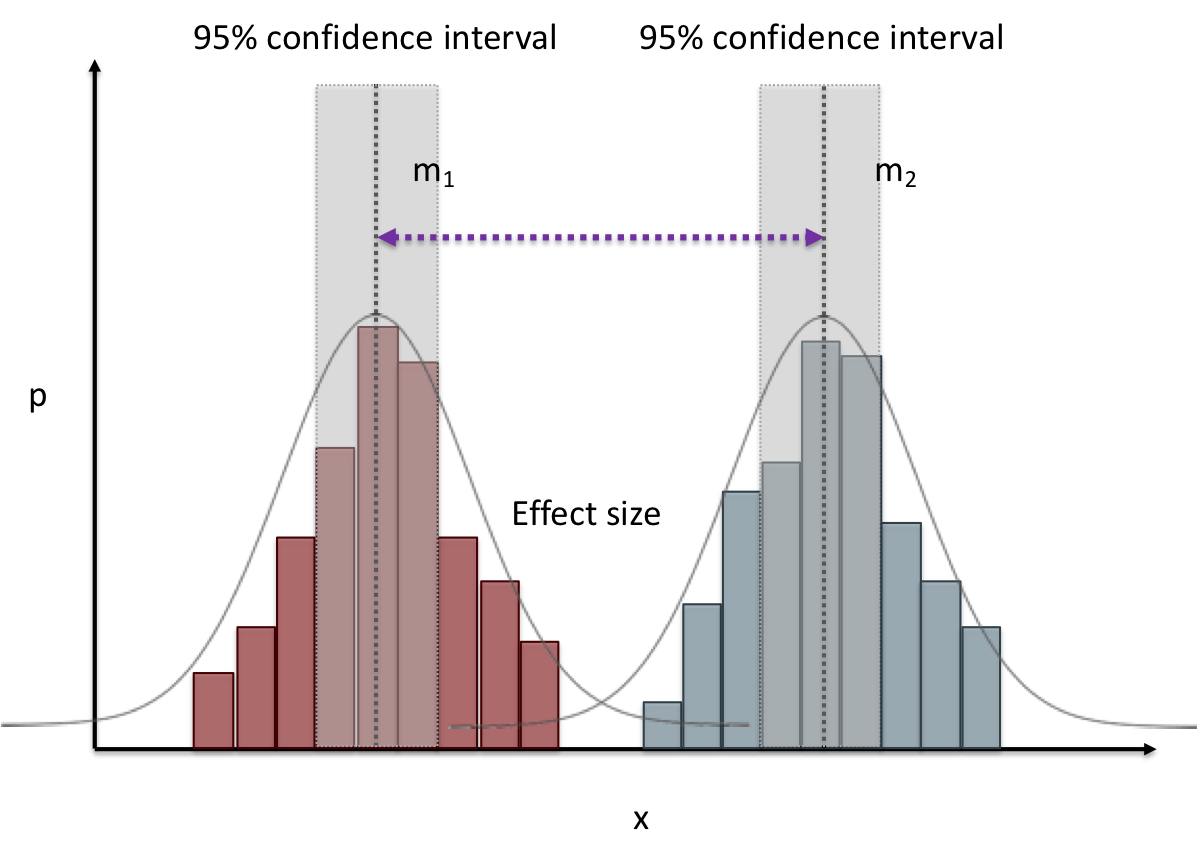 --- # Common Statistical Test for comparison: t-test Tests for difference between two samples Best used to determine what is ‘worthy of a second look’ Limited in its applicability to normal, independent data Does not help to document effect size [the actual difference between groups], just effect likelihood --- .left-column[ ## Problems with t-tests The more implausible the hypothesis, the greater chance that it is a ‘false alarm’ ] .right-column[  ] ??? Top row: Prior (what's known to be true before the experiment) bottom row: Calculated p-value Notice the middle column, where something that is a toss-up has higher plausability than we would expect. This is a "Type 1 error" Alternatively, a small sample may cause a Type II error (failure to detect a true difference) due to random sampling bias --- exclude: true .left-column[ ## Problems with t-tests ] .right-column[ - Doesn’t take prior knowledge into account - Susceptible to ‘data dredging’ - The more tests you conduct the more likely you will find a result even if one is not there - Adjustments mid experiment - Gives a yes or no answer: Either the null hypothesis is rejected (the result would be unlikely in a world where the null hypothesis was true) or it cannot be rejected - Based on assumed ‘average’ sample ] --- exclude: true # Which problems might affect our study? ??? Too many comparisons -- count: false 18 separate comparisons (3x3 conditions, 2 measures) ANOVA (**An**alysis **O**f **Va**riance): Fancy t-test that accounts for the whole group effect before doing pairwise comparisons ??? - Doesn’t take prior knowledge into account - Susceptible to ‘data dredging’ - The more tests you conduct the more likely you will find a result even if one is not there - Adjustments mid experiment - Gives a yes or no answer: Either the null hypothesis is rejected (the result would be unlikely in a world where the null hypothesis was true) or it cannot be rejected - Based on assumed ‘average’ sample --- # Demo of t-tests in our spreadsheet [23wi Sample data](https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1LDFGu_2EFCd-jCgK0JhkLWTGk3aTNg2jKwf6Fr0TJws/edit?usp=share_link) --- # Document what all of this in your [report](/courses/cse340/23sp/assignments/menu-report) Speed Results `Describe your thoughts about overall speed in different conditions. Use at least one chart to illustrate what you say. Here is an example chart generated using our data, when you paste your data into the spreadsheet you’ll see that it updates to reflect your data` Error Results `Describe what happened in terms of errors -- provide at least one chart showing what you learned about errors in different conditions` --- .left-column[ ## Document what all of this in your [report](/courses/cse340/23sp/assignments/menu-report) ] .right-column[ - Describe your hypothesis - Illustrate with graphs - Optional: use Table of results found in `Speed Analysis` and `Error Analysis` to describe Statistical Significance: `Pie menus were twice as fast as normal menus (M=.48s vs M=.83s), F(1,43)=295.891, p < .05. Unclassified menu items were harder to find than linear and relative ones (M=.84s, .59s, and .59s respectively), F(2,43)=93.778, p < 0.5. We also found an interaction effect between menu and task (as illustrated in the chart above), F(5, 43) = 51.945, p < .001.` ] --- # Using the right chart matters .left-column40[  ] .right-column50[ |Normal | Pie| |--|--| ||| ] --- # Can we determine *causality*? We'd like to be able to argue the task/menu type influenced the speed and error results. -- This implies *dependence* between speed/error, task, and menu type -- And it assumes you have measured the right variables! --- # Drawing Conclusions <div class="mermaid" style="font-size:.5em"> graph LR S(.) --> Hypothesis(Hypothesis:<br>Decreased seek <br>time and errors) Hypothesis -- "Study Design" --> Method(3 menus x <br> 3 task conditions ) Method -- "Run Study" --> Data(Data) Data -- "Clean and Prep" --> Analysis(Analysis) Analysis --> Conclusions(Conclusions) classDef finish outline-style:double,fill:#d1e0e0,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px,font-size:.7em,height:2.5em; classDef normal fill:#e6f3ff,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px,font-size:.7em,height:2.5em; classDef normalbig fill:#e6f3ff,stroke:#333,stroke-width:2px,font-size:.7em,height:4em; classDef start fill:#d1e0e0,stroke:#333,stroke-width:4px,font-size:.7em,height:5em; classDef startsmall fill:#d1e0e0,stroke:#333,stroke-width:4px,font-size:.7em,height:2.5em; classDef invisible fill:#FFFFFF,stroke:#FFFFFF,color:#FFFFFF linkStyle 0 stroke-width:3px; linkStyle 1 stroke-width:3px; linkStyle 2 stroke-width:3px; linkStyle 3 stroke-width:3px; linkStyle 4 stroke-width:3px; class S invisible class Hypothesis start class Conclusions startsmall class Method normalbig class Data,Analysis normal </div> - Describe your hypothesis - Illustrate with graphs - Optional: Statistical Significance Draw Conclusions - Were errors less? - Was time faster? `Describe your conclusions. Do you think we should use pie menus more? What can we conclude from your data?` --- # Limitations of Laboratory Studies ??? Simulate real world environments - Location and equipment may be unfamiliar to participant [Coyne & Nielsen 2001] - Observation may effect performance - “Hawthorne Effect” [Mayo 1933] - Participant may become fatigued and not take necessary rest - “Demand Effect” [Orne 1962] - Tasks frequently artificial and repetitive, which may bore participants and negatively effect performance Studying real world use removes these limitations -- Simulate real world environments - Location and equipment may be unfamiliar to participant [Coyne & Nielsen 2001] - Observation may effect performance - “Hawthorne Effect” [Mayo 1933] - Participant may become fatigued and not take necessary rest - “Demand Effect” [Orne 1962] - Tasks frequently artificial and repetitive, which may bore participants and negatively effect performance Studying real world use removes these limitations