layout: false [//]: # (Outline Slide) # Today's Agenda **Do this now**: Answer the [poll](https://edstem.org/us/courses/21053/lessons/31192/slides/180606) in Ed Administrivia - Undo out, due Fri 20-May, 10pm Learning goals - Define pursuasion, coersion - Discuss the role of mobile devices on behavior change - Design a mobile app to encourage users to change their car usage --- name: inverse layout: true class: center, middle, inverse --- # [NOTIFICATIONS](http://sitn.hms.harvard.edu/flash/2018/dopamine-smartphones-battle-time/)  .footnote[Picture from [itstimetologoff.com](https://www.itstimetologoff.com/2018/03/22/why-switching-off-your-social-media-and-phone-notifications-is-your-own-mini-digital-detox/)] ??? Multiple kinds of notifications on your phone. Here's the red dot with the number of messages on it. What other kinds are there? - Toast - appears within an app only - Email? Easy or hard to ignore What do you prefer? Which are more interruptive? Urge to clear the red dots on the screen? They effect your brain the seritonin in your rain (red dots in particular) --- layout: false # Recent Examples .left-column-half[ Glucose Buddy   ] .right-column-half[ Facebook 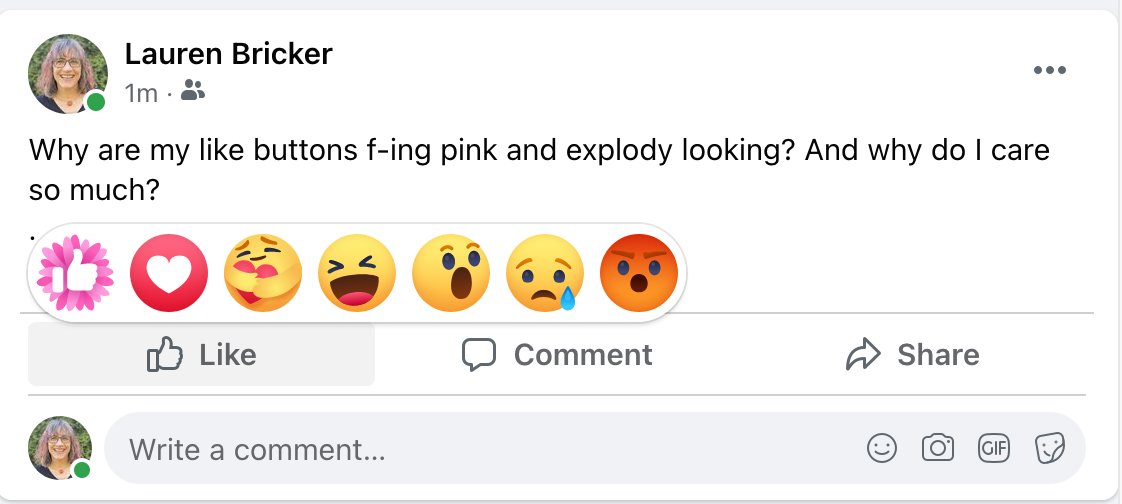 ] --- # Recent Examples .left-column-half[ Ed  ] .right-column-half[ <br> <br> How does this make you feel? ] --- # [Dopamine, Smartphones & You: A battle for your time](http://sitn.hms.harvard.edu/flash/2018/dopamine-smartphones-battle-time/) 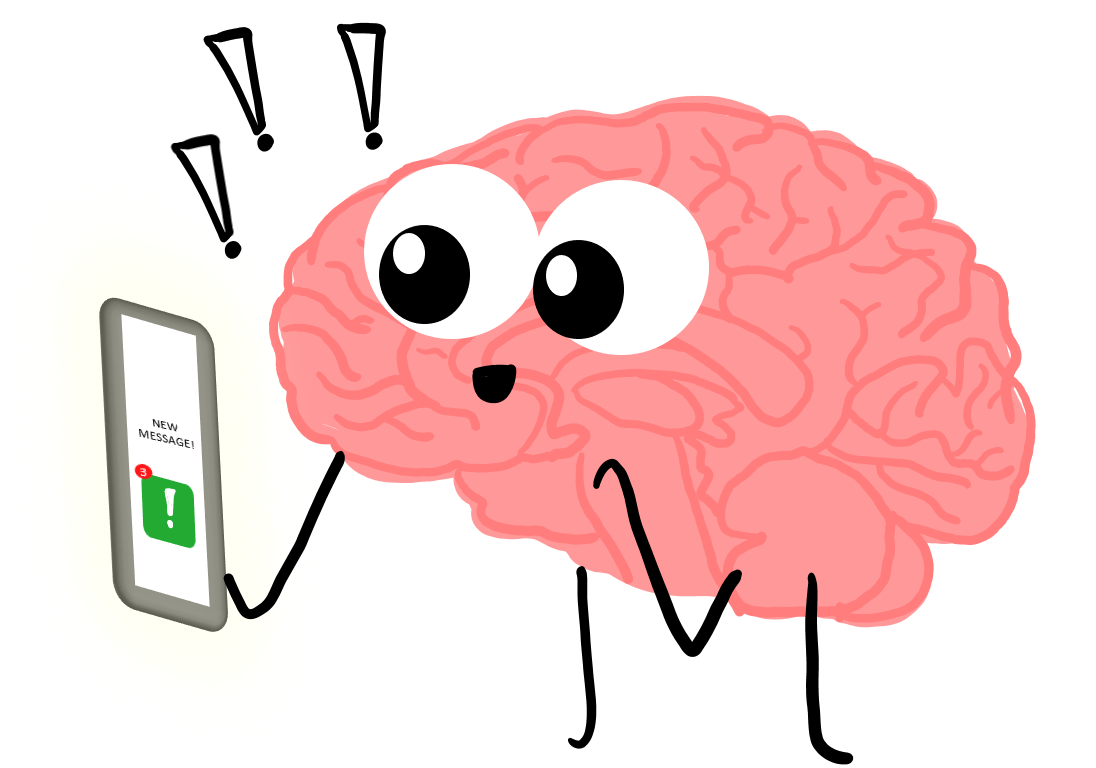 ??? From a company's perspective, it's trying to get your attention Not an altruistic service It's not always the case, but incentives are there. War between companies to get your attention Important to think about how you use notifications if you're doing Mobile app development. --- layout: false .left-column[ ## Using Mobile Phones to Persuade Lauren Bricker CSE 340 Spring 2022 ] .right-column[  ] --- # What does it take to persuade you? ![:youtube Wildebeest arguing about a log and whether it is a crocodile, JMJXvsCLu6s] --- # Technology for persuasion .left-column-half[ 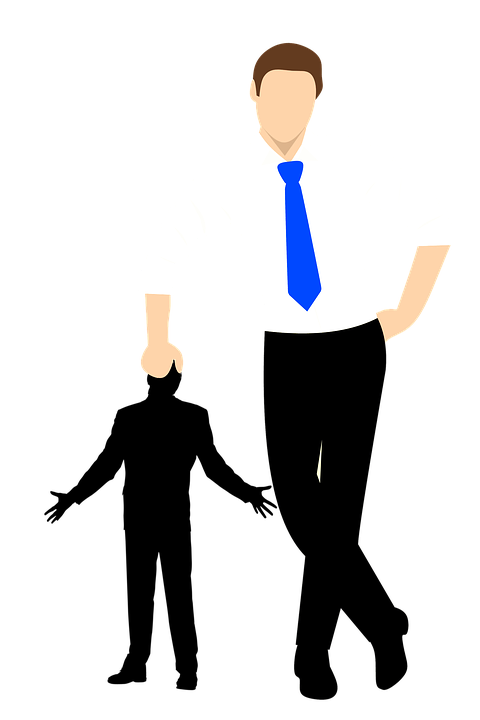 ] .right-column-half[ Coercive : negative connotations, patronizing, paternalistic, "we know what’s best for you and you will do it!" ] -- count: false .right-column-half[ Persuasive : convincing you to change your behavior. ] --- # Technology for persuasion .left-column-half[ Which do you think is true? - Persuasive is the same as Coercive - Persuasive is better than Coercive - Persuasive is worse than Coercive - Persuasive is not the same (but not better or worse) than Coercive ] .right-column-half[ Coercive : negative connotations, patronizing, paternalistic, "we know what’s best for you and you will do it!" Persuasive : convincing you to change your behavior. ] -- count: false .right-column-half[ Think of technology that pursuades you to do some kind of action. ] ??? If you've bought something like a fitbit, you're buying into the idea of something pursuading you to do something. --- # What does it take to persuade you? ![:youtube People being persuaded to climb stairs, 2lXh2n0aPyw] -- count: false - Is this coercive or not coercive? -- count: false - What kind of pursuasion is being applied here. --- # What does it take to persuade you? .left-column-70[ ![:youtube Cialdini on Pursuation, cFdCzN7RYbw] :54 6 shortcuts ] ??? Tip example - How are they doing the study? What are the conditions? What are they measuring? (how much they tip) How do they sample? Are they consenting the participants like we have to do the menus study? --- # What does it take to persuade you? How does this list of shortcuts apply to interface design? - reciprocity - scarcity - authority - consistency - liking - consensus -- count: false **Goal** - can we get people to keep using your product - can we get people to get other people to use your product --- # What’s needed to support positive behavior change? .quote[ If you cannot measure it, you cannot improve it.] Lord Kelvin --- # Ties to Sensing and Security Almost every app that you download collects data about you. - Most of the data they're collecting is through third party libraries. - Data collected through seemingly benign apps. - Example: Angry birds collects location data, why? Some apps use sensor based interfaces - what can we do with sensor data? ??? Angry birds => Sales --- # Data Collection Options  --- # Data Collection Options .left-column[ Or we could just use one... ] .right-column[  ] ??? We're carrying this around and letting them collect all this data. --- .left-column[ ## Making Data Actionable ## Data ] .right-column[  ] --- .left-column[ ## Where is the value? ## Data ] .right-column[ Most of what we get is Data  ] ??? We have to do more to turn the raw into something useful. Knowledge instead of just data --- .left-column[ ## Making Data Actionable ## Knowledge ] .right-column[ This might make you slow down...<br>  ] --- count: false .left-column[ ## Making Data Actionable ## Knowledge ] .right-column[ This might make you slow down...<br>  <br>Unless you're a cyclist... <br>  ] --- .left-column[ ## Making Data Actionable ## Decision Making ] .right-column[  ![:fa quote-left] Danger... you have exceded the speed limit of 80kph. Slow down immediately or face strict disciplinary action ![:fa quote-right] .footnote[[Meru speed alarms in cabs](https://www.meru.in/about-us/our-philosophy)] ] ??? This will be influencing based on the data --- .left-column[ ## Making Data Actionable ### Translating data into behavior change ] .right-column[  Website that had a list of all the APIs that researchers were aware of (at the time) that supported behavior change. ] .footnote[[personalinformatics.org](https://web.archive.org/web/20190729114530/http://www.personalinformatics.org:80/tools/)] ??? --- .left-column[ ## Making Data Actionable ### Translating data into behavior change ] .right-column[ Conference paper: A Stage-Based Model of Personal Informatics Systems.  Developed with 68 survey participants, 11 follow-up interviews ] .footnote[Li, Dey, Forlizzi. CHI 2010.] ??? Study done at the iSchool Beyond notifications to get users to use an app Can't assume that everyone is at the action stage. --- .left-column[ ## Preparation  ] .right-column[ <br> <br> Alex! - **Wanted** to become active - **Decided** to track their physical activity - **Chose** to track step counts using a pedometer ] .footnote[ **Preparation**|Collection|Integration|Reflection|Action] --- .left-column[ ## Collection ] .right-column[ | day | steps | day | steps | day | steps | day | steps | day | steps | day | steps | |-----|-------|-----|-------|-----|-------|-----|-------|-----|-------|-----|-------| | Mon | 1573 | Mon | 1209 | Mon | 12344 | Mon | ... | Mon | ... | Mon | ... | | Tue | 4392 | Tue | 1834 | Tue | 1200 | Tue | ... | Tue | ... | Tue | ... | | Wed | 4537 | Wed | 4341 | Wed | 4311 | Wed | ... | Wed | ... | Wed | ... | | Thu | 5842 | Thu | 8300 | Thu | 7348 | Thu | ... | Thu | ... | Thu | ... | | Fri | 10258 | Fri | 10300 | Fri | 9384 | Fri | ... | Fri | ... | Fri | ... | | Sat | 7528 | Sat | 6347 | Sat | 5123 | Sat | ... | Sat | ... | Sat | ... | | Sun | 1367 | Sun | 1231 | Sun | 1430 | Sun | ... | Sun | ... | Sun | ... | | Mon | 1497 | Mon | 1503 | Mon | 1427 | Mon | ... | Mon | ... | Mon | ... | | Tue | 1837 | Tue | 1717 | Tue | 1643 | Tue | ... | Tue | ... | Tue | ... | | Wed | 4537 | Wed | 4341 | Wed | 4311 | Wed | ... | Wed | ... | Wed | ... | | Thu | 5842 | Thu | 8300 | Thu | 7348 | Thu | ... | Thu | ... | Thu | ... | | Fri | 10258 | Fri | 10300 | Fri | 9384 | Fri | ... | Fri | ... | Fri | ... | | Sat | 7528 | Sat | 6347 | Sat | 5123 | Sat | ... | Sat | ... | Sat | ... | | Sun | 1367 | Sun | 1231 | Sun | 1430 | Sun | ... | Sun | ... | Sun | ... | | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ] --- .left-column[ ## Integration  ] .right-column[  ] .footnote[ Preparation|Collection|**Integration**|Reflection|Action] ??? bar plot --- .left-column[ ## Reflection  ] .right-column[  ] .footnote[ Preparation|Collection|Integration|**Reflection**|Action] ??? Days when she's really outside of the mean --- .left-column[ ## Action  ] .right-column[ The stage when people choose what they are going to do with their new-found understanding of themselves. ] .footnote[ Preparation|Collection|Integration|Reflection|**Action**] ??? How can we support this with technology? -- count: false .right-column[ - Alerts - Incentives - Suggestions ] ??? Context-aware computing... --- .left-column50[  ] .right-column50[ # Why Behavior Change is Difficult **Every stage presents distinct barriers** Failures in one stage cascade through later stages, must design for entire tracking process **This occurs in a larger context of deciding to track, selecting a tool, and eventual lapsing** ] .footnote[Epstein, Ping, Fogarty, Munson. A Lived Informatics Model of Personal Informatics. UbiComp 2015.] ??? Fitbit users lapse after a time - they don't charge it. Not incentivised. Have to account for when they're lapsing --- # Process of Change  -- count: false - Using the same plan for every individual who wishes to change a behavior will not work - Timing is important in the process of willful change --- .left-column40[ # Case Study: <BR> Energy Use ] .right-column60[  ] --- # What is the responsibility of technologists to address climate change?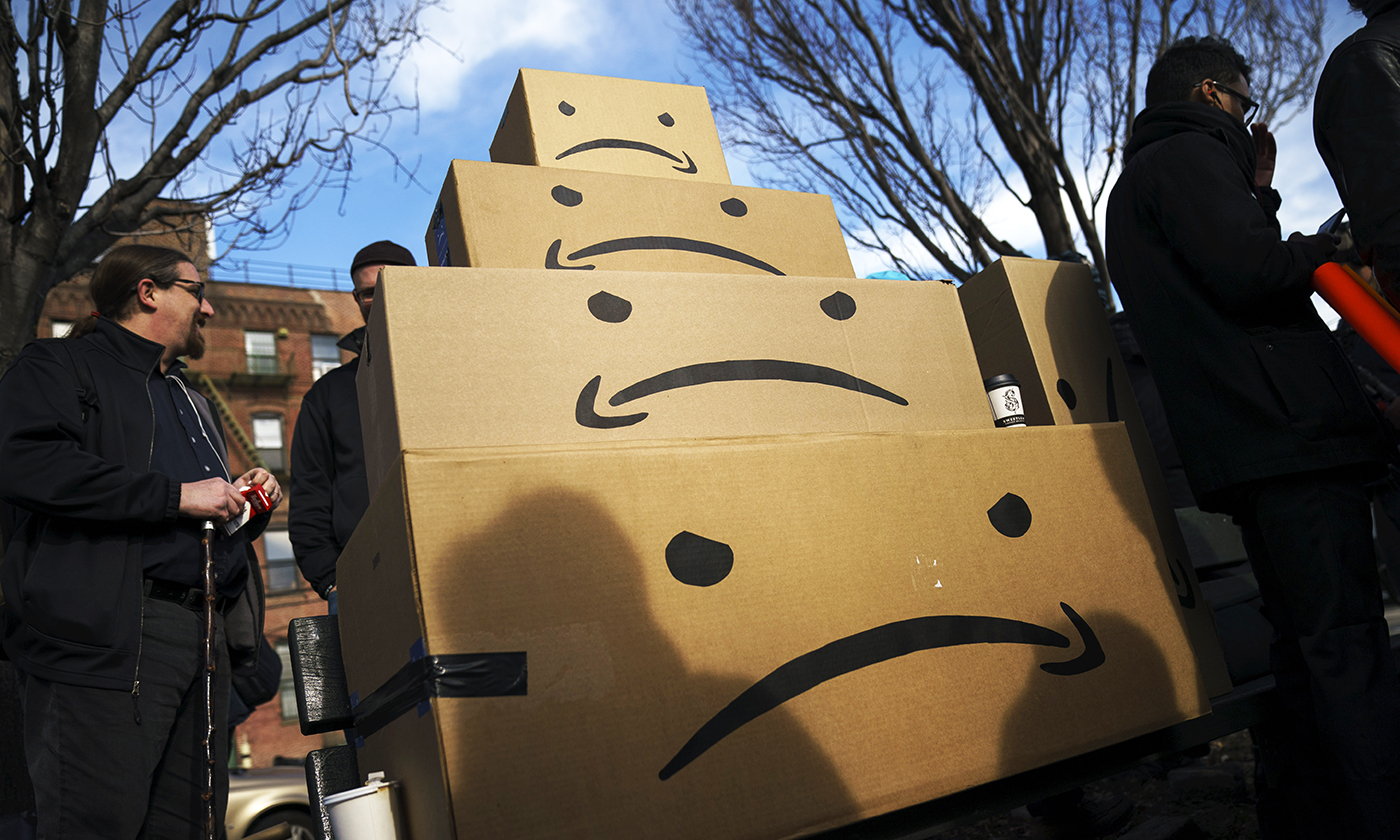  .footnote[[Amazon Refuses to Act on Climate Change. So We Employees Are Speaking Out](https://www.yesmagazine.org/planet/amazon-climate-change-action-jeff-bezos-20190530)] --- # Case Study: UbiGreen - In Class activity .left-column30[ 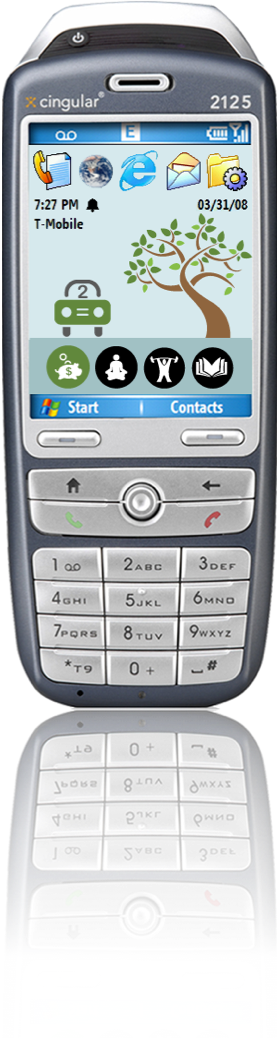 ] This will be fun - a design activity! -- count: false Honest. -- count: false Each group will work on [slide](https://edstem.org/us/courses/21053/lessons/26124/slides/152232) that is in our Ed lesson for today. The case study is explained on the next slide AND in the lesson. -- In each group - One person should be the note taker - One person should be elected to share out when the time comes. --- # Case Study: UbiGreen - In Class activity .left-column30[  ] Problem: High Carbon Dioxide emissions from U.S. households from personal transportation (single use vehicles). Goal: To create an app that will encourage users to change their behavior with respect to using their cars. -- This was last done in 2006-9... the app needs updating... .footnote[ based on a [CHI 2009 paper](https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/1518701.1518861) by J. Froehlich, T. Dillahunt, P. Klasnja, J. Mankoff, S. Consolvo, B. Harrison, J. A. Landay ] --- # Case Study: UbiGreen - In Class activity .left-column30[  ] .right-column70[ Your task: - Design an app that will - Use sensing data to determine a user's behavior (what type of data would you need?) - Persuade (or coerce?) users of your app to change their behavior - Design a user study that will determine if your app is successful. - What is your [hypothesis](/courses/cse340/22sp/slides/wk06/menus-experiment.html#23)? - What is your [method](/courses/cse340/22sp/slides/wk06/menus-experiment.html#26)? What conditions might you have for your experiment? - What might you [measure](/courses/cse340/22sp/slides/wk06/menus-experiment.html#27)? - What [data](/courses/cse340/22sp/slides/wk06/menus-experiment.html#28) would you collect? - How would you [collect the data](/courses/cse340/22sp/slides/wk06/menus-experiment.html#29)? - How would you prove your theories? ] --- # Case Study: UbiGreen - actual research .left-column30[  ] .right-column70[ Sensed Transportation Behavior Ever-present Feedback Two formative studies - Online survey - In situ experience sampling method (ESM) study Three week field deployment ] .footnote[ based on a [CHI 2009 paper](https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/1518701.1518861) by J. Froehlich, T. Dillahunt, P. Klasnja, J. Mankoff, S. Consolvo, B. Harrison, J. A. Landay ] ??? Smartest phone at the time (2006) --- # Case Study: UbiGreen - actual research  --- # Case Study: UbiGreen - actual research 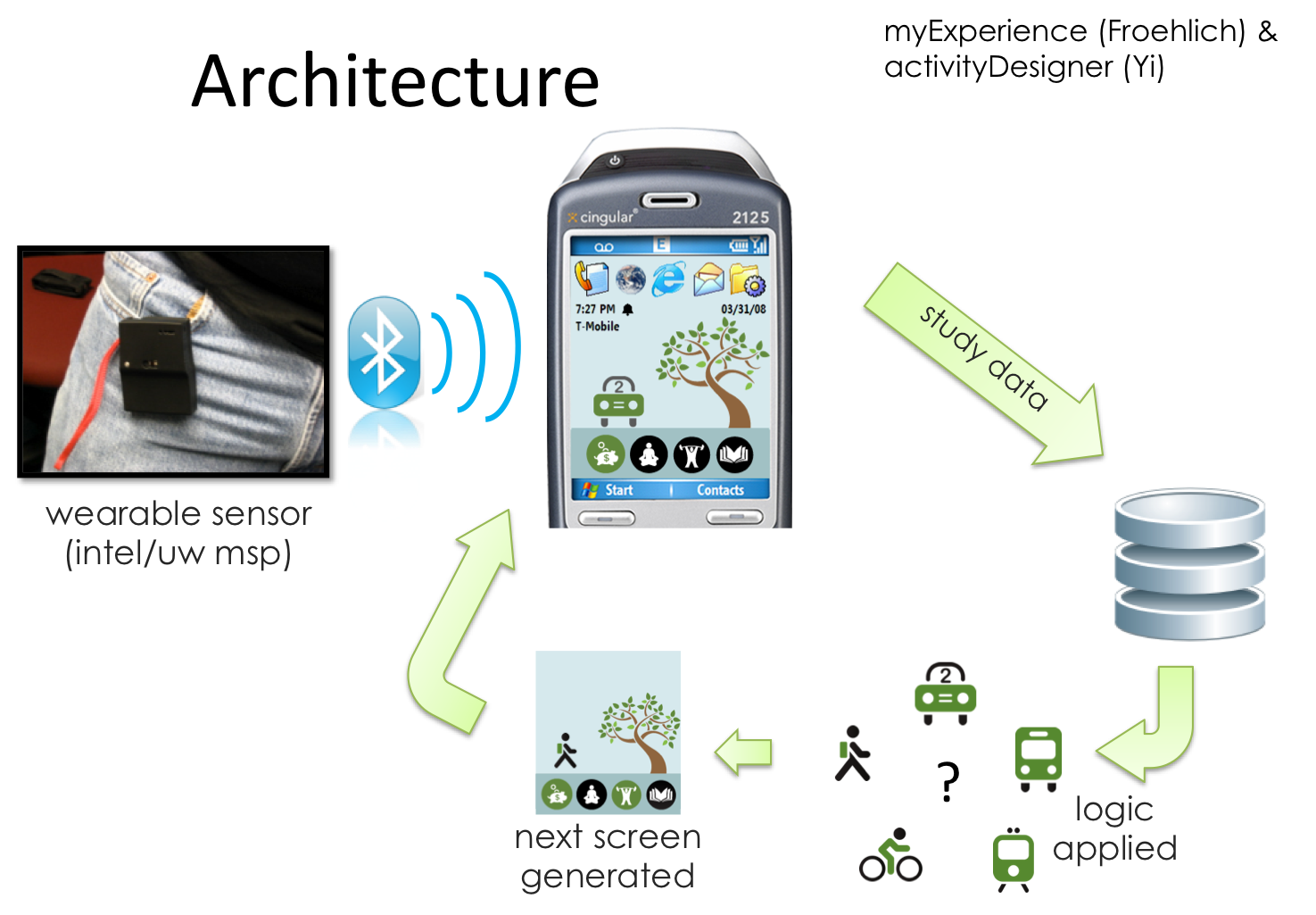 --- # Case Study: UbiGreen - actual research  --- # Case Study: UbiGreen - actual research .left-column[  ] .right-column[ 2 cities; 14 participants Obtain preliminary feedback on prototype - Engagement - Potential for social use - Potential for changing behavior ] --- # Case Study: UbiGreen - actual research .left-column[  ] .right-column[ Engagement .quote[It's omnipresent] Behavior Change: .quote[ “It really encourages you to analyze your own performance” ] <!-- Social .quote[ “Some people at work knew about the polar bear and every day they --> <!-- asked me about it. ‘Did you get a seal today?’”] --> ] ??? Introspection --- # Personal Informatics  ??? Apply it to ubigreen --- # End of Lecture Content The next few slides are an aside on other ways for CS to engage with sustainability --- # CS and sustainability .left-column50[ Impact: Direct ways of reducing carbon emissions - Efficiency (new technologies, new patterns of use, better buildings, etc.) - Carbon capture & storage - Alternate sources of energy - Carbon sinks (e.g. reforestation) - Better energy grid ] .right-column50[ Solutions: Indirect ways of reducing carbon emissions - Population control - Economic controls (e.g., taxes) - Cross-cultural solutions (culturally-relevant technologies) - Education - Governmental buy in (Local laws, world treaties, etc) - Advancing science ] .footnote[ [Socolow & Pacala](http://ngm.nationalgeographic.com/2007/10/carbon-crisis/img/stabilization_wedges.pdf); A. Gore, Earth in the Balance ] --- .right-column[ ## Checklist for Nobile ICT<sup>*</sup> Impact .footnote[<sup>*</sup> ICT = Information and communications technology] *Measure* waste and impact - Example: [what happens to phones when you finish with them?](https://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?doid=1357054.1357110) *Monitor, Model & Inform* governments as well as individuals - Example: [Measuring air pollution using a mobile device](https://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?doid=1978942.1979290) ] --- .left-column[ <br> 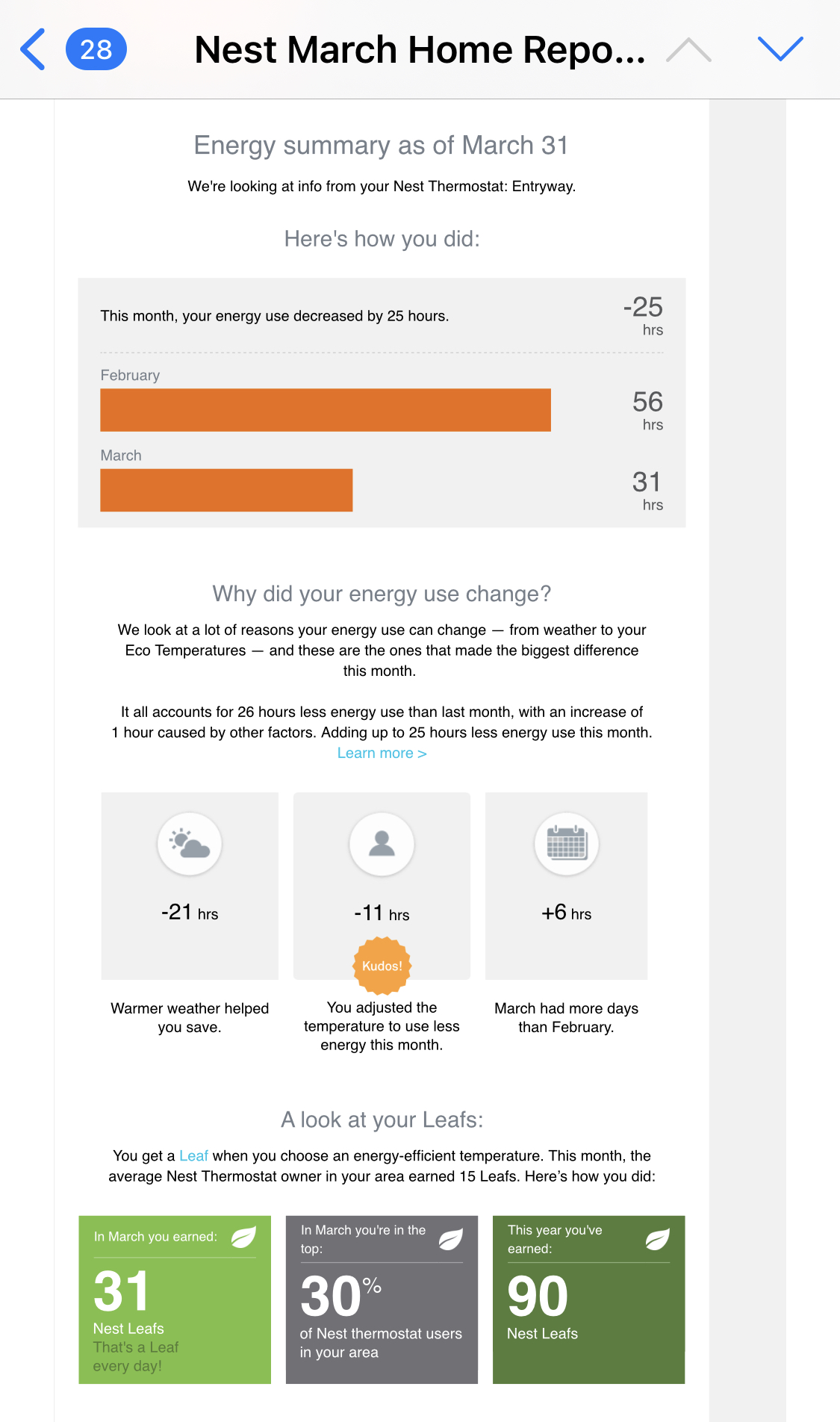 ] .right-column[ ## Checklist for mobile ICT impact *Encourage environmentality* - example [Automated thermostat setting](https://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?doid=2493432.2493441) - automation, efficiency, re-use - people (lived experience) - reduce waste ] .footnote[[some computer science issues in creating a sustainable world](http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~io/publications/ieee08-preprint.pdf)] --- .left-column[ <br> 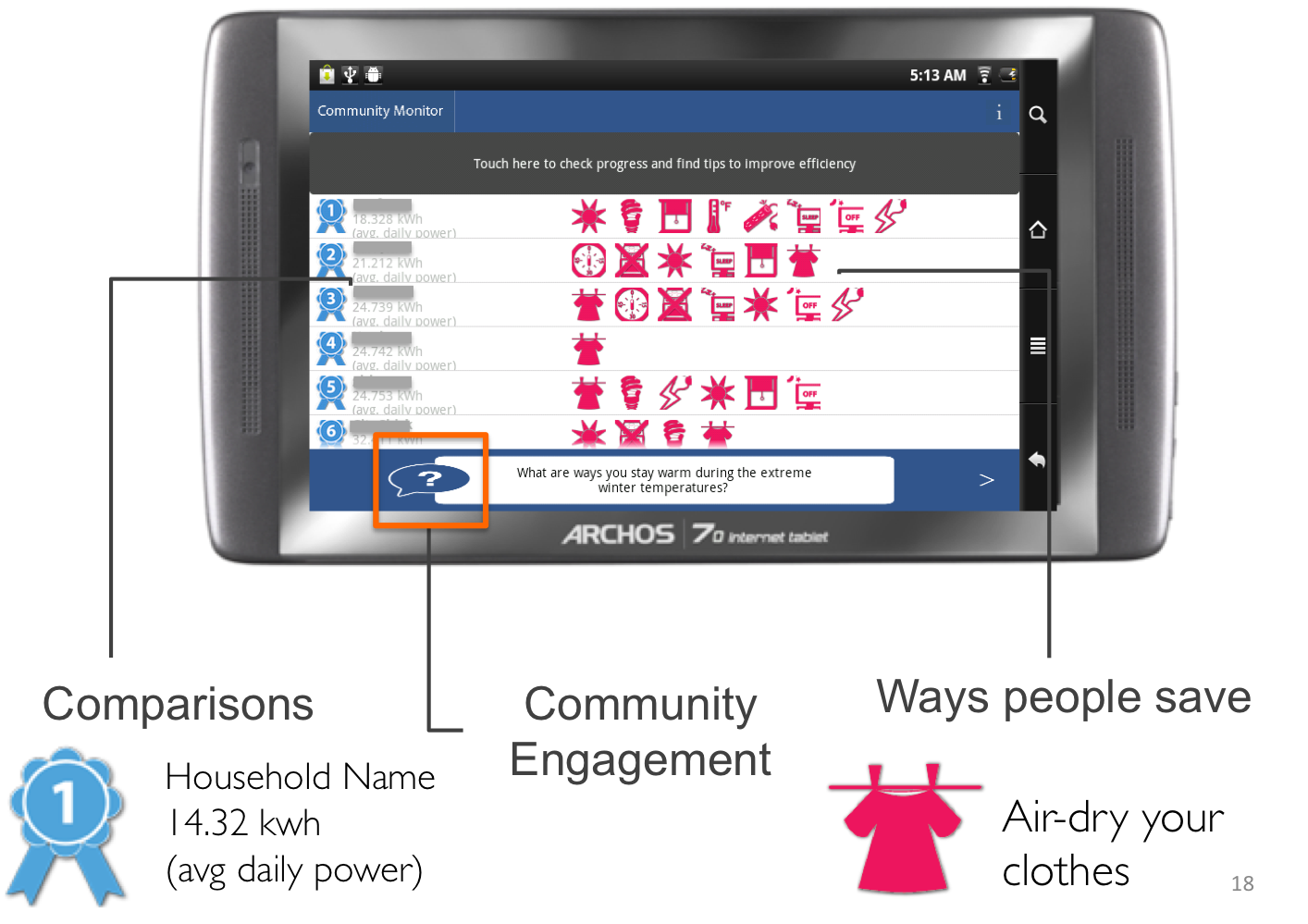 ] .right-column[ # Checklist for mobile ICT impact *Relevance across sectors and cultures* (residential: (renters, owners, etc), business, ...) - Example: [understanding conflicts between landlords and tenants around energy use](https://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?doid=1864349.1864376) - Example: [deploying an android energy monitor to help communities & individuals monitor](https://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?doid=2531602.2531626) Goal: *Scale up* to governments, nations or more ] .footnote[ [Some computer science issues in creating a sustainable world](http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~io/publications/ieee08-preprint.pdf) ] --- .title[Why a digression on sustainability in a behavior change lecture?] .body[  ] ??? That's all there is to fix it, we need the will power at a society level Of course there's other applications of behavior change as well :) Health is a big one!