name: inverse layout: true class: center, middle, inverse --- # Introduction to Drawing Jennifer Mankoff CSE 340 Winter 2021 --- layout: false [//]: # (Outline Slide) # Today's goals - Administrivia - Warmups - Checks for understanding - Quick view of resources - Abstractions for drawing on the screen - Drawing in Android - Clipping and other transformations --- ## Developer roles .left-column[ <div class="mermaid"> graph LR ip[Interface Programmer] w[Component Developer] l[Library Extender] a[Architecture Extender] t[Toolkit Builder] classDef yellow font-size:14pt,text-align:center classDef green font-size:14pt,text-align:center class t,l,a,w yellow class ip green </div> ] .right-column[ From [last class](first-app.html) we briefly discussed of the roles a developer can play in app development. - Today we're going to focus on being an *Interface Developer* (adding existing components like `CircleView` to your doodle) - We might get to touch on being a *Component Developer* and thinking about how to create that new `LineView` component ] --- # Drawing on the Screen - Take out your phone. Open an App. What do you see on your screen? --- # What is on your screen? .left-column50[ 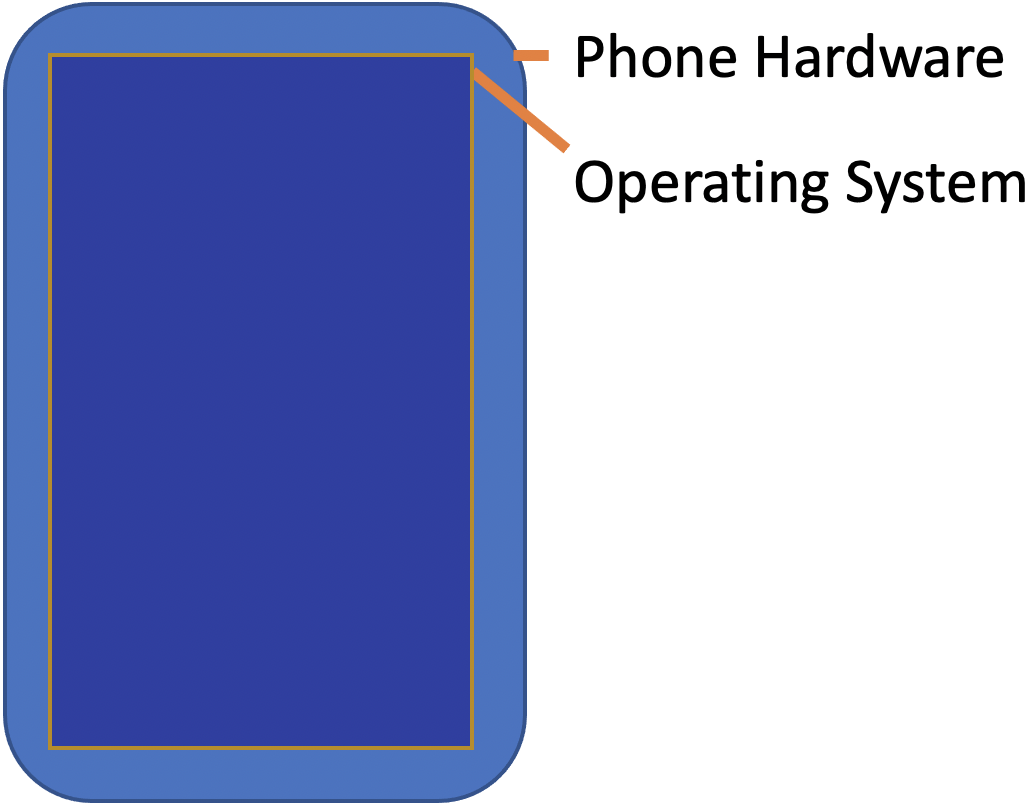 ] --- # What is on your screen? .left-column50[ 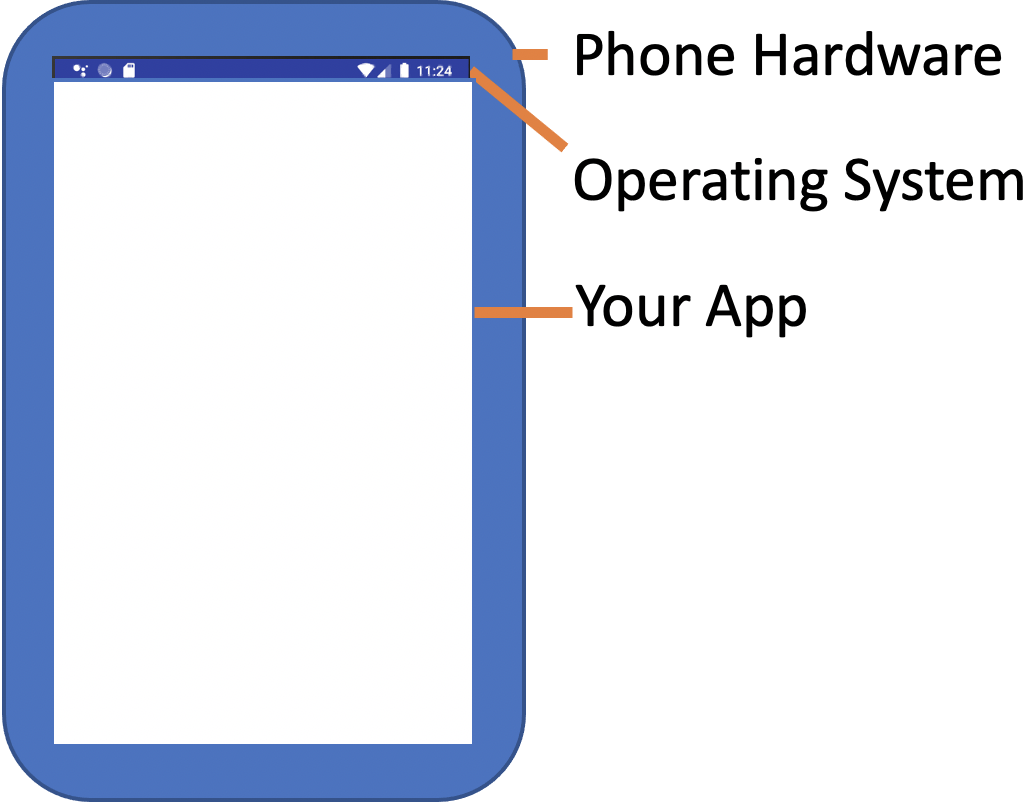 ] --- name: poll-everywhere # What is on your screen? .left-column[ 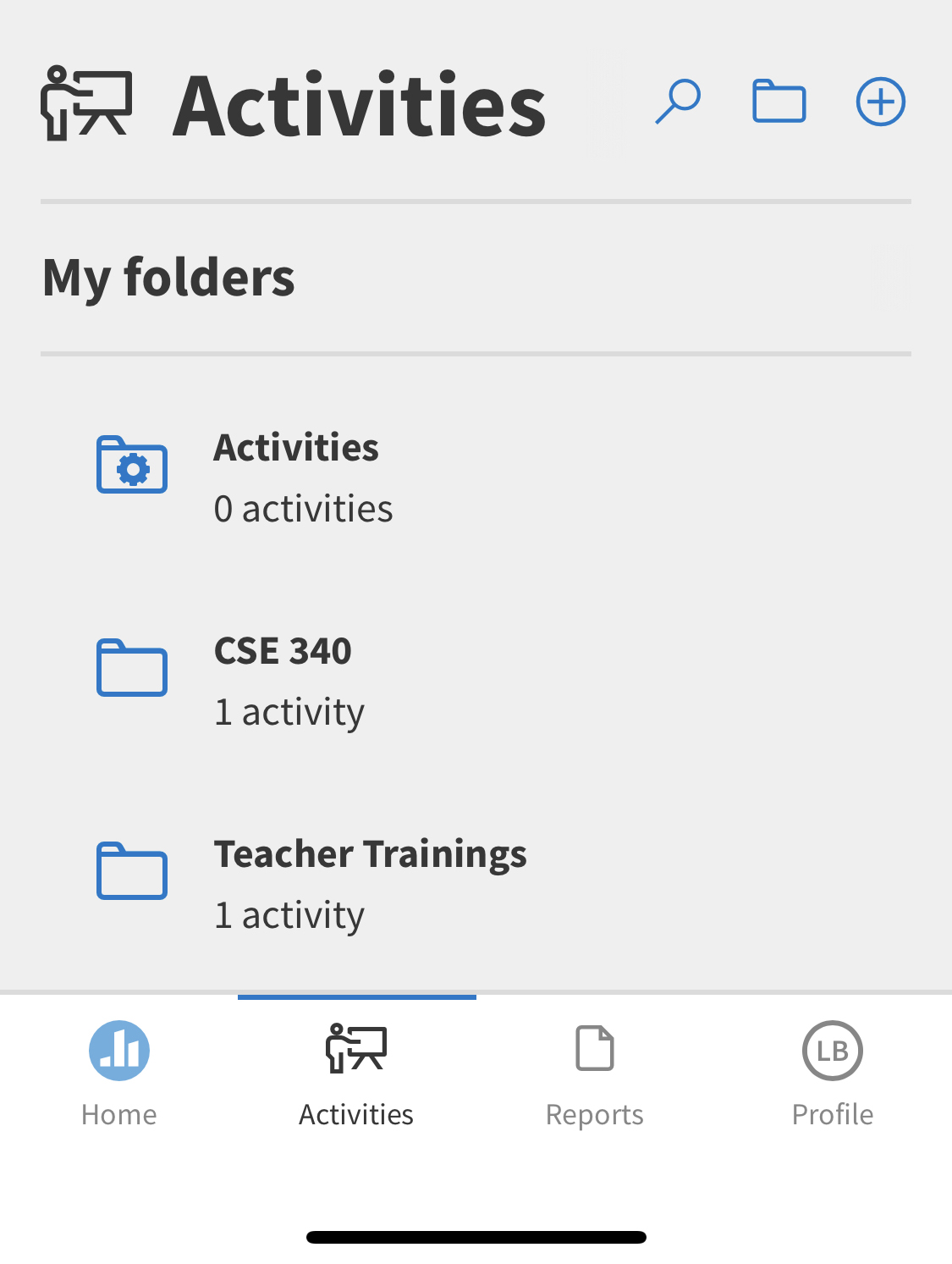] ??? This is what I see in poll everywhere What is an app made up of? --- template: poll-everywhere .right-column[ App is made up of? *Components* Last class we discussed the "tree" of components. Think about what this hierarchy might look like. - What is at the "root" ? - How is this divided up into sections - In each section, how are things further divided up? ] --- template: poll-everywhere .right-column[ <div class="mermaid" style="width: 100%"> graph TD W(Window) --> T[Title Bar] W --> L[Label: My Folders] W --> F[Folders] W --> B[Toolbar] T --> TA[Icon] T --> TB[Label: Activities] T --> TC[...] F --> F1[Folder 1] F --> F2[...] F1 --> I[Icon] F1 --> N[Folder Name] F1 --> C[Activity Count] B --> H[Button:Home] B --> A[...] B --> R[Button: Reports] B --> P[Button: Profile] class W start class T,L,F,B,TA,TB,TC,F1,F2,H,A,R,P,I,N,C blue </div> ] --- template: poll-everywhere .right-column[ App is made up of? Components What are components made up of? ] ??? Should push them down to the lowest level on the screen App is made up of? Components Components are made up of? lines, circles, text Lines, circles and text are made up of? Pixels --- template: poll-everywhere .right-column[ App is made up of? Components Components are made up of? lines, circles, text Lines, circles and text are made up of? Pixels (picture elements) ] --- # Aside: Displaying a Pixel .row[ .column[ Do you know how pixels are lit up in color or greyscale? - on your computer or TV screen? - on a projector? ] ] --- # Aside: Displaying a Pixel .row[ .column[ Do you know how pixels are lit up in color or greyscale? - on your computer or TV screen? - on a projector? ] .doublecolumn[ [Cathode Ray Tube](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cathode-ray_tube) | [LED Display](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/LED_display) :--: | :--:  |  ] ] ??? Get them to at least realize that the actual pixels on their screen are LEDs --- # Toolkit Support for Basic Drawing .left-column[ ] .right-column[ All toolkits have some sort of `Canvas` object or abstraction - `Canvas` is an object level abstraction for performing drawing operations - Each *Component* (`View`) has a `Canvas` in Android - You can access it in the `onDraw(Canvas canvas)` method *Aside: Components Widgets, Interactors, and `Views` are all variations on the same term* ] ??? Connect to DrawingPanel in 143? In Android, we call these components `Views` --- # Toolkit Support for Basic Drawing .left-column[ ] .right-column[ When is `onDraw()` called? - Handled automatically for you by toolkit - Triggered whenever the pixels are *dirty* (there's been a change to what needs to be viewed) - You can trigger this with `invalidate()` (we'll use this in the future) ] ??? Lots to discuss here. Mainly focus on introducing the concept of a library (a bunch of components you can pick from, Canvas and its methods, etc) vs an architecture (which controls when and in what order things happen). We'll learn about both in this class. You need to understand both to use a toolkit. --- # How does Canvas work? - Drawing is done by calling methods for different kinds of objects -- count: false - For example: `drawRect`, `drawOval`, `drawLine`, `drawPath` ... [Full List in the API Documentation](https://developer.android.com/reference/android/graphics/Canvas.html) --- # What is on your screen, Doodle Edition .row[ .column[  ] .doublecolumn[ <div class="mermaid" style="width: 100%"> graph TD Part1B(Part1BActivity) --> C1[Circle1] Part1B --> C2[Circle2] Part1B --> Cd[...] Part1B --> C9[Circle9] Part1B --> Text[Test Page] Part1B --> I1[Image1] Part1B --> Id[...] Part1B --> I4[Image4] Part1B --> L1[Line1] Part1B --> Ld[...] Part1B --> L4[Line8] class Part1B start class C1,C2,Cd,C9,Text,I1,Id,I4,L1,Ld,L4 blue </div> ] ] --- # What is a component's coordinate system? .left-column[  ] --- # The standard coordinate system - (0,0) is at the top left of the screen - The screen is drawn pixel by pixel from top left to bottom right in "raster" lines   [Source: Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Analog_television#Displaying_an_image) --- # What is a component's coordinate system? .left-column[  ] .right-column[ Every view thinks `(0,0)` is at the top left of its bounding box (the minimal box that encloses that view) Doodle has lots of views! ] --- # Aside: Bounding box of an object A bounding box (or sometimes [Minimum Bounding Box](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Minimum_bounding_box)) is a term used in coordinate geometry to describe the smallest rectangular area that contains an object or set of objects. Great example to play with: https://www.mathopenref.com/coordbounds.html --- # Bounding Boxes What are the coordinates for the top left corner of the bounding box of a line that goes from (15, 10) to (0, 10)? ??? Why not 15,10? Why not 0,0 ( ) (0, 0) ( ) (15, 10) (X) (0, 10) ( ) (15, 15) ( ) (10, 10) --- # What is a component's coordinate system? .left-column[  ] .right-column[ If the radius of the top left CircleView is 100 pixels - What are the coordinates of the circle's top left corner *in its parent coordinates*? ] --- # What is the top left corner of a circle? .left-column[  ] .right-column[ Android's [Canvas](https://developer.android.com/reference/android/graphics/Canvas) `drawCircle()` is specified using center x, center y and radius ```java // Draw the specified circle using the specified paint. void drawCircle(float cx, float cy, float radius, Paint paint) ``` When we say *top left corner* we are really referring to the circle's bounding box's top left corner. ] --- # Revisit of quiz question Which is a valid corner for a bounding box for a circle created using the android Canvas to [drawCircle(10, 10, 10, p)](https://developer.android.com/reference/android/graphics/Canvas#drawCircle(float,%20float,%20float,%20android.graphics.Paint)? ??? ( ) (10, 10) ( ) (10, 20) (X) (0, 0) ( ) (20, 10) --- # Quiz feedback Most wrong answers were people who didn't answer - This is practice for examlets. - It also helps me target lecture to things you struggle with Most questions on this quiz were answerable with reading the documentation - We've tried to minimize required readings - This is stuff you'll need to understand to do your assignments In sum: Please take the time to do the required readings and quizzes. It will help you; it will help us help you. --- # What is a component's coordinate system? .left-column[  ] .right-column[ If the radius of the top left CircleView is 100 pixels - What are the coordinates of the circle's top left corner *in its parent coordinates*? - What is the CircleView's parent? ] --- # What is a component's coordinate system? .left-column[  ] .right-column[ If the radius of the top left CircleView is 100 pixels - What are the coordinates of the circle's top left corner *in its parent coordinates*? ] --- # What is a component's coordinate system? .left-column[  ] .right-column[ If the radius of the top left CircleView is 100 pixels - What are the coordinates of the circle's top left corner *in its parent coordinates*? - What are the coordinates of the circle's top left corner *in child coordinates*? ] --- # What is a component's coordinate system? .left-column[  ] .right-column[ If the radius of the top left CircleView is 100 pixels - What are the coordinates of the circle's top left corner *in its parent coordinates*? - What are the coordinates of the circle's top left corner *in child coordinates*? - What is the circle's *center* in *child coordinates*? ] --- # Aside: Why so many separate `Components`? .left-column[  ] .right-column[ Useful when we want to do animation Also provides **separation of concerns** and good high level control - Can have a different paint object for each view - Can easily change z-order (what is on top of what) - Can store information used to draw that thing (whatever it is) - Can either make the size of the whole screen or resize around what is drawn Views can also be re-used easily ] ??? This could be a good place to ask them to think about what that means and demonstrating two things with different z order. --- # Building an interactor from scratch .left-column[  ] .right-column[ (remember -- interactor = interactive component, <br>or `View`) ] --- # What does a component need to do? .left-column[  ] .right-column[ *Draw on the screen* <BR> using [*Canvas*](https://developer.android.com/reference/android/graphics/Canvas) *Handle input* <BR>(we won't do this until the *fourth* assignment, colorpicker) ] --- # How do we use Canvas in Doodle? .row[ .column[ <div class="mermaid" style="width: 670px; height: 271px;"> classDiagram ImageView <|-- DrawView DrawView <|-- CircleView DrawView <|-- TextView DrawView <|-- LineView class DrawView { +getBrush() #initFromParentCoords() #onDraw() } </div> ] .doublecolumn[ - `DrawView` can draw on screen (and be moved around). You will implement part of it. It inherits from [View](https://developer.android.com/reference/android/view/View) and can draw images. - You will implement subclasses `CircleView`, `TextView` and `LineView`. ] ] ??? Green: Android toolkit Blue: Classes we provide you don't have to modify Yellow: Classes you implement Remind students that they did do inheritance in 142/143 like with Critters. --- # How does Canvas work? - Drawing is done by calling methods for different kinds of objects - Lots happens under the covers... let's look at an example... -- count: false "I want to draw a line on the screen" -- count: false So I would likely call `drawLine` on the `Canvas`. -- count: false So... how do I tell the computer where the start and end of the line will be? --- # Things to think about Drawing Demo - things to think about - What is the bounding box of a line that is drawn diagonally - from upper left to lower right? - lower right to the upper left? - from the upper right to the lower left? - from the lower s` - What is bounding box of a vertical line? - What is the bounding box of a horizontal line? --- # How is a drawing object rendered on screen? - An object (like a line) would be converted into one or more **strokes** - A stroke has properties such as width or color - The stroke is converted to **pixels** (correspond to dots on your screen) - These pixels are put in a `Bitmap` (frame buffer) first, then updated on the screen all at once ??? top left is from old-style raster graphics, where a beam of light literally moved down the screen from top left to bottom right, causing chemical excitation when on and thus lighting the screen the last is left over from when both graphics and drawing were slower and more linear Still most reliable approach --- # How is a stroke converted to pixels? - Strokes (can be) size independent. Pixels are not - Strokes are continuous. Pixels are not - Anti-aliasing Essentially converting from **vector** to **raster** graphics ([Bresenham's algorithm](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bresenham%27s_line_algorithm)) --- # Quick understanding test What internal data structure (abstraction) represents an entire picture to display on a color screen? -- pixels in a 2D array  Pixel Calculator (Tanimoto 2010) ??? **A frame buffer (2D array) (picture)** The following are wrong, they represent a single pixel (but we haven't studied this yet) - A pixel (R,G,B) - A number from 0 to 255 --- # What is the [Paint](https://developer.android.com/reference/android/graphics/Paint.html) Object? .left-column[  ] .right-column[ A Paint object is an abstraction that determines how drawing operations should look ```java Paint drawPaint = new Paint(); drawPaint.setColor(Color.BLUE); drawPaint.setAntiAlias(true); drawPaint.setStrokeWidth(5); drawPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE); canvas.drawCircle(500, 500, 400, drawPaint); drawPaint.setStrokeJoin(Paint.Join.ROUND); drawPaint.setStrokeCap(Paint.Cap.ROUND); drawPaint.setColor(Color.GREEN); drawPaint.setStrokeWidth(15); canvas.drawLine(350, 300, 500,600, drawPaint); ```] --- # What is the [Paint](https://developer.android.com/reference/android/graphics/Paint.html) Object? - Abstraction that determines how drawing operations should look - Drawing style: stroked, filled - Line Characteristics: color, line width, join, cap styles - Fill Characteristics (color)    --- # Other Paint properties - Text Characteristics: font family, style, size, alignment settings, etc. -- count: false - Font: shapes for chars (called *glyphs*) plus layout - family or typeface  --- count: false # Other Paint properties - Text Characteristics: font family, style, size, alignment settings, etc. - Font: shapes for chars (called *glyphs*) plus layout - family or typeface - style: plain, *italic*, **bold**, **_both_**, ~~strikethrough~~, *etc.* -- count: false - points: 72.27 points per inch ??? because french inches were different (72 per inch) Really just a guideline these days It is the *width* of a capital M (no height specified) --- # The Path Object - Canvas supports drawing primitive shapes _and_ arbitrary paths: `void drawPath(Path p, Paint paint);` -- count: false - Declaring a `Path` can be done by combining basic primitive shapes (e.g rectangles, circles, ovals, curves like arc, cubic, etc.) -- count: false - **What drawing model** does creating a path in this way correspond to? - Raster model - Vector model --- count: false # The Path Object - Canvas supports drawing primitive shapes _and_ arbitrary paths: `void drawPath(Path p, Paint paint);` - Declaring a `Path` can be done by combining basic primitive shapes (e.g rectangles, circles, ovals, curves like arc, cubic, etc.) - **Which is more scalable?** - Raster model - Vector model ??? XXXX could do in-class [drawing exercise](https://github.com/mriveralee/ssui-mobile-exercises-2016/tree/master/exercises/lab05/CustomDrawing) IF time XXXX needs updating --- # Summary & revisiting learning goals for this week - What is on the screen: Hardware, OS, App, Components - Component Tree (Interactor Hierarchy) - Pixels (lots of dots) - Coordinate systems in parents and children - Bounding boxes - Canvas & Paint & Paths in Android - Pixel & stroke models