React Tips and Tricks
Contents:
- Introduction
- React Tips
- JS / Web Development Tips
Introduction
This page contains a number of tips and tricks for using React and Javascript to develop web applications in 331. These include brief primers on web topics that are beyond the scope of this course but might come in handy, deeper looks at some React features that are important, and some Javascript tidbits that might explain some confusing errors.
React Tips
These tips go into detail about some of the finer points of building an application with React that will be useful for the React assignments. You should read this section before beginning work on your CampusPaths program, and it's highly recommended that you read it before attempting the Map Lines warmup assignment.
Advanced User Interface (Text Boxes, Dropdowns, etc.)
Fully-Controlled Components
React modifies the way some native HTML user interface elements work to make them more compatible with the core ideas behind React. These modifications are detailed in React's Forms documentation, but what follows is a more directed and less technical explanation of the changes, and how components like text fields, drop-down boxes, and other data-bearing UI elements should be used.
In regular HTML, elements like <input> are used to create text boxes. These
elements naturally maintain some internal state: the text contained within the text box. Updates to
the currently-contained text (such as when a user types a character into the box) are handled in an
unsurprising way: parent components pass a function to the onChange prop, and that
function is called with a parameter containing an Event object. That event object
contains lots of information about what happened to cause the event, including the new contents of the
text field inside event.target.value (event.target gets the <input>
element that's the "target" of the event, and the value field of an input element
contains its current value).
In this way, <input> elements are similar to buttons, they're created and use
callbacks to inform their parents of interesting UI events (like a click or a change in text).
However, <input> elements differ from buttons in that they also function as a "live
display" of the current value - you can see the text inside a text field. In traditional
HTML, this functionality is maintained inside the <input> element, and the
user doesn't have to worry about it. However, this means that the "source of truth" about what the
data inside the element is, is actually inside the <input>. This doesn't work well
for React, which likes to have parents "control" the data and be the single source of truth. In React,
data likes to flow "downward" (from parent to child) - it's the entire model.
To allow these components to be more usable with React, they were modified so that
<input> elements (and other elements that display data that they are responsible
for changing) take a value prop in addition to the onChange prop. This
value prop forces the <input> (or other component) to take on the
value that's being provided to it. It will always contain exactly that value. This means that
the "source of truth" about the value of the <input> can be stored inside the
parent component, and simply passed to the <input> as a prop - the <input>
blindly accepts this data as the truth, and our friendly React developers at Facebook can put their
pitchforks away and return to their desks.
See the image below for a diagram of this data flow. It can be easier to think of the <input>
element as a hybrid of two separate elements inside the same tag - one which is responsible for
detecting and receiving keyboard input, and communicating that to the onChange handler
appropriated, and the other is simply responsible for displaying whatever text is passed into the
value prop - conveniently located in a click-able box. It's up to the parent component to
communicate the data from one side to the other - the parent receives updates about what the user is
typing into their keyboard, and is responsible for changing its stored value accordingly, and passing
that value back to the <input> to be displayed to the user: so the key they typed
actually shows up on the screen.
In the example, anything inside the blue box is a part of the <input>, and the
banner at the top is the value of the text box stored inside the parent component, likely in the
parent component's state. Keyboard events detected by the <input> trigger a call to
the onChange callback, which communicates the user's requested change to the
parent. The parent then can call setState (or otherwise update the currently-stored
value) to store the change and notify the <input> element's "display side" to show
the new text for the user - ready for the next keypress. While the description above is long, as data
is flowing through multiple methods and components, it's important to remember that this entire
process happens in tiny fractions of a second, and it appears that the text shows up in the box
immediately as the user presses the key.
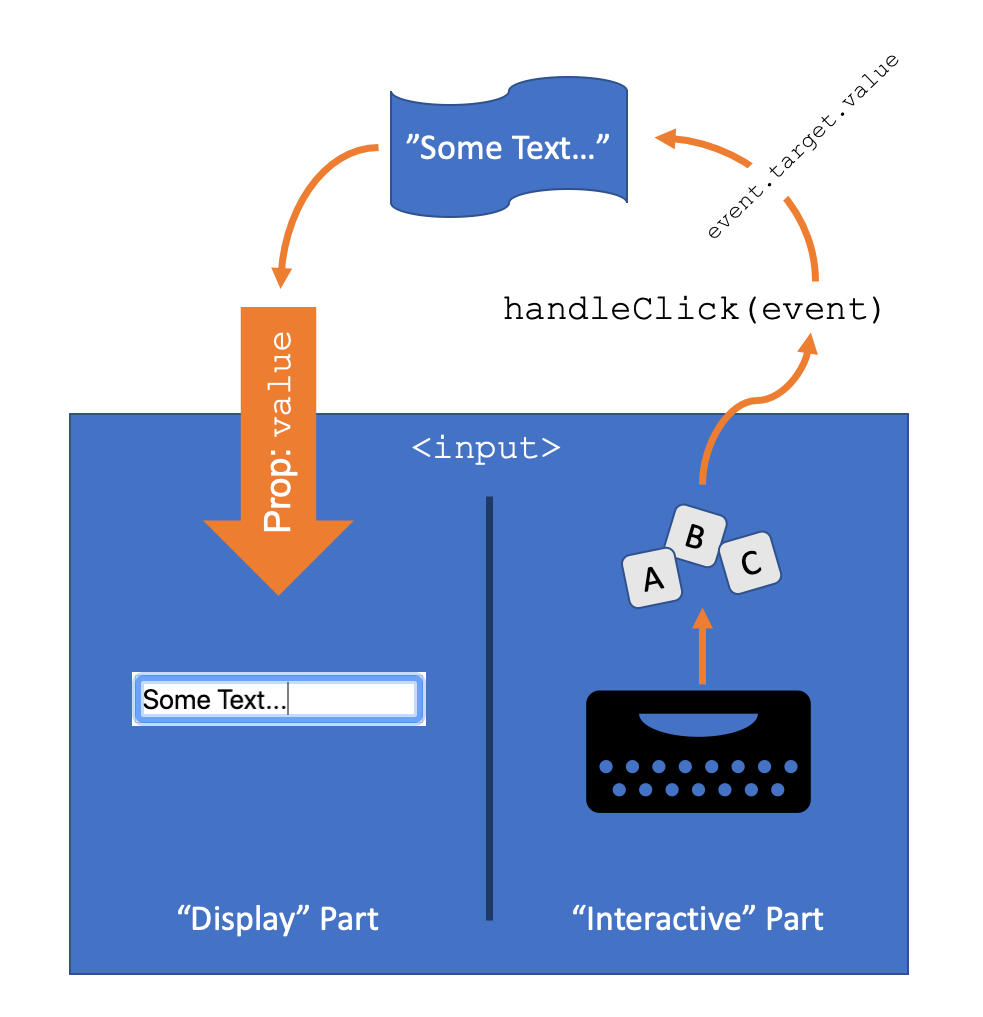
React calls this model - where the actual data is stored elsewhere and the UI elements act as fancy
interactive displays - a fully-controlled component model. The <input>
element is controlled by its parent, and simply exists to abstract away the logic involved in decoding
keyboard events and dispatching them as change events. In contrast, the traditional HTML
usage of <input> elements is called "uncontrolled."
Note that this model of only updating the form data through an event handler is quite powerful. Since
it's the parent component's responsibility to update the "truth" about the current value of the <input>,
it's completely free to choose not to do so, or modify the text as it's being entered. For
example, an input component with a value specified to some literal effectively cannot be edited -
typing with the component selected will send events to the onChange handler, but there's
no way to change the actual value inside the input. Consider the following un-editable input:
<input value="Unchangeable" onChange={() => console.log("ignoring change...")} />
A more interesting example might be the following:
// State initialization and other component code omitted for space.
handleInputChange = (event) => {
this.setState({
inputValue: event.target.value.toUpperCase()
});
};
render() {
return (
<input value={this.state.inputValue} onChange={this.handleInputChange} />
);
}
In the above example, all text is converted to uppercase as the user types it - regardless of what character they actually typed.
Dropdowns and other Select-type Elements
Dropdowns and other selector-type elements behave similarly to <input> as described
above with regards to their value being stored in the parent and the controlled-component model.
However dropdowns manage their list of selectable options in a slightly unintuitive way that's
described here. Each option has both a "value," and a piece of "display text" that's actually shown to
the user. Think of these as key-value pairs in a map data structure: the "value" of the option is the
key, and the "display text" is the value. (Yes, that's confusing naming, we know.) The display name
for the option is what's used to actually display the option to the user inside a drop-down box, while
the value of the option is what's actually returned in onChange handlers, stored
in state, and used for computation. This allows you to have pretty display names to make life easier
on your users, without having to use large, clunky strings for actual computation inside the code.
An example drop-down menu is shown below, with the currently-selected item being the option describing
pears. Notice that the value and onChange props function identically to the
elements described above.
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
selected: "pear"
};
}
handleChange = (event) => {
// Ignoring all changes because pears are always the best. :)
};
render() {
return (
<select value={this.state.selected} onChange={this.handleChange}>
<option value="orange"> I love oranges. </option>
<option value="apple"> Apples are my favorite. </option>
<option value="pear"> Pears are the best. </option>
</select>
);
}
Text Fields Contain Text
Yes, this seems like something obvious, but it's easy to forget in practice - especially when using
"filtered" input types. For example, you can declare an <input> that only accepts
numerical input using the "type" attribute, but the actual returned value from the input is always a
string, and will behave as a string in code. Consider the following:
// Other component code omitted for space.
handleChange = (event) => {
this.setState({
inputValue: event.target.value;
});
// Also, let's print out our number plus 6:
console.log(event.target.value + 6);
};
render() {
return (
<input type="number" value={this.state.inputValue} onChange={this.handleChange}>
);
}
In this example, entering the number "1" into the text field is perfectly valid - the text field is configured to allow numeric input, and "1" is numeric input. However, the number 7 is not printed to the console. Instead, the string "16" is printed - the number 6 is converted to the string "6", which is concatenated with the already-was-a-string-value "1". Since the text field always gives us a string, we have to be careful when we're using it for other kinds of input.
The parseInt() function
can come in handy with situations like this. Make sure to read its documentation before using it - it
has interesting behavior when the string isn't parsable as a number, or is only
partially-parsable.
You Probably Don't Need a <form> Tag
Many pieces of documentation about <input> elements and other UI elements use them
inside a <form> tag, which allows them to be used as part of a larger web form. Web
forms are useful because they are specially tied with a unique submit button, and can automatically
send requests to server with form data when the submit button is pressed, such as a sign-in form on a
website's homepage.
For our purposes, we're only building single-page applications, so web-form logic is generally
unnecessary. The UI components will all work fine (and fire their onChange and onClick
handlers properly) outside a <form>, so think twice before copy/pasting code that
uses form tags, and consider whether you really need the additional behavior provided by them.
Returning Multiple Elements from render
Sometimes, we want our components to render into multiple HTML tags, instead of just a single tag.
Unfortunately, Javascript - like Java - doesn't allow returning more than one thing from a function.
Fortunately, we can use our grouping elements, like <div> and
<span>, to combine multiple elements together as children of a single parent
element, then use that parent element as the "one" element we're returning from our
render method. See below:
render() {
return (
<div>
<p>I'm an element!</p>
<p>I'm another element!</p>
</div>
);
}
State Updates Are (Shallow) Merges
When updating state, the object being passed to setState actually represents a list of
"changes" to be applied to current state, instead of a completely new state object that will replace
the old one. This is because setState actually performs a shallow merge of the new state
into the old one. It's a merge, because properties inside the state object are replaced by their
counterparts in the new state object (or created if they didn't already exist), but existing
properties that aren't mentioned inside the new state object are left unchanged. It's a shallow merge,
because objects contained within state are not merged, but simply replaced completely - the merging
only happens one level "deep" into state. Consider the following examples, showing state before and
after a successful state update.
Note that, for simplicity of writing the examples, updated state values are shown
immediately after the call to setState. Because state updates are actually
requests, it is not correct to expect the new values to be present in this.state
immediately after a call to setState. This example is not meant to imply that
state values update immediately – assume that the "after" version of state is being shown
after the state update has propagated completely and componentDidUpdate has been called.
// state == {
// thing1: 17,
// thing2: true
// }
this.setState({
thing1: 42,
thing3: "hello, world"
});
// state == {
// thing1: 42, // modified
// thing2: true, // untouched, thing1 and thing3 were merged in without removing thing2
// thing3: "hello, world" // added, didn't already exist
// }
this.setState({
thing4: { // thing4 is another object inside the state object
subThing1: true
subThing2: "i'm inside two layers of objects!"
}
});
// state == {
// thing1: 42,
// thing2: true,
// thing3: "hello, world",
// thing4: {
// subThing1: true
// subThing2: "i'm inside two layers of objects!"
// }
// }
this.setState({
thing4: {
subThing1: false
}
});
// state == {
// thing1: 42,
// thing2: true,
// thing3: "hello, world",
// thing4: { // subThing2 is now missing, the entire thing4 object was replaced
// subThing1: false
// }
// }
If you find yourself in a situation where you need to perform a deep merge, you'll need to implement
it yourself. In the example above, you could get the current value of the entire thing4
object, modify the subThing1 value while leaving the subThing2 value
unchanged, then use the new "modified" thing4 to replace the entire thing4
object with setState's shallow merge, as normal. Note that if you're performing
this kind of deep merge with the previous contents of state, you'll need to use the alternate version
of setState described in the Advanced Usage of setState
section, below.
Advanced Usage of setState
setState can be more complicated than it seems on the surface due to its functionality as
a request to update state instead of an immediate update to state. The most common bug we see
with state in 331 is when students attempt to use state immediately after setting it, instead of only
using it when a component update is happening (i.e., when inside componentDidUpdate). For
example, the following pseudocode will generally not draw the correct thing to the screen:
drawPath() {
let path = findPathFromAtoB(...);
this.setState({
displayedPath: path
});
this.drawPathToCanvas(); // <- This is wrong. Reading path directly after setting it usually won't work.
}
If you assume that the drawPathToCanvas function is relying on the value of this.state.displayedPath
to work, then the above code likely will not have received the state updated by the time drawPathToCanvas
has completed, and therefore it won't be able to draw the correct path. A corrected version would look
something like this:
drawPath() {
let path = findPathFromAtoB(...);
this.setState({
displayedPath: path
});
}
componentDidUpdate() {
if(this.state.displayedPath !== null) { // or some other check to see if there _is_ a path to draw
this.drawPathToCanvas();
}
}
In addition to this basic behavior of setState requiring some care while organizing your
code, there are some additional nuances introduced by this behavior that are discussed here. In
particular - since in certain situations (whenever you're not "inside" a component update) you can't
trust that the current value of this.state is up to date, you can't use that value when
trying to decide the new value of state. That is - you can't normally use the
current value of state when calculating the new value of state. (If you're in a
situation where you know for sure that state is up-to-date, then you don't have to worry
about this, of course.)
A simple example of the issue is a situation where we have a single button that we want to toggle some
state value: if the value is true, the button makes it false, and vice
versa. An incorrect implementation would be below:
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
toggleValue: false
};
}
onButtonClick = () => {
this.setState({
toggleValue: !(this.state.toggleValue) // <-- This is incorrect!
});
};
render() {
return (
<button onClick={this.onButtonClick}>Toggle the Value</button>
);
}
Notice how the current value of state is being used to calculate the new value inside the setState
call. Now, since setState is simply a request, it may take React some time to actually
complete the state update. So what happens if the user presses the button twice before React has a
chance to complete the state update? The "current value" of state will be incorrect for the second
setState call - causing the calculated value for the new state to be incorrect as well.
Effectively, one of the two button presses will be ignored. See the example timeline below:
* button press *
this.state.toggleValue == false
setState({toggleValue: true})
* button press *
this.state.toggleValue == false // it's possible that React hasn't completed the state update yet.
setState({toggleValue: true})
* state update completes some time later *
this.state.toggleValue == true
// User pressed the button twice - it should have gone back to `false`, but it's `true`
The React developers understood that many developers will want to be able to use the current state to
create a new state, so they introduced a different version of setState that solves this
problem. This new version takes a function instead of an object, and it uses
that function to calculate the new state. The key difference is this: that function also gets two
arguments: prevState and prevProps. Unlike the value of
this.state, the value of prevState is guaranteed to be up-to-date,
so it's safe to use it in your code. Let's modify the onButtonClick function in the above
code to use this new version of setState:
onButtonClick = () => {
this.setState(this.stateToggler);
};
stateToggler(prevState, prevProps) {
return {
toggleValue = !prevState.toggleValue // <-- Safe because prevState is guaranteed to be up-to-date
};
}
In the above example, we wrote a separate "state updater" function that takes the two arguments - the guaranteed-to-be-updated previous state, and the guaranteed-to-be-updated previous props, and returns the correct new value of state based on the up-to-date previous value. This was written as a separate function for clarity for this example, though you'll almost always see the following version written in actual React code:
onButtonClick = () {
this.setState( (prevState, prevProps) => {
return { toggleValue: !prevState.toggleValue };
});
};
This version works the same way, it just writes the "updater" function as an arrow function directly
inside the call to setState. Since we always use a guaranteed-up-to-date copy of
state when we're calculating the new state, we'll never miss/skip a value and the bug described above
has been fixed! For more information, you should check out the
React documentation describing this version of setState, as well as the formal documentation of setState()
(kinda like setState's "javadoc").
The React Component Lifecycle
Every React component has a lifecycle - it is created, rendered, changed, updated, and removed in a
specific sequence that's defined as that component's lifecycle. The most common lifecycle methods
that'll be used in 331 are componentDidMount and componentDidUpdate, which
are called after mounting and updating a component. "Mounting" is the process that a component goes
through when it's created by React, initialized, and inserted into the webpage. "Updating" is what
happens to a component when something about its state or properties that would require the component
to be re-rendered.
Consult a diagram of describing the React component lifecycle (like this one) for a detailed overview as to the structure and order of lifecycle methods. The most important thing to be aware of about the lifecycle is where you are in the lifecycle at any given point in the code. (It's also possible to be "nowhere" in the lifecycle, such as when inside an event handler for a button click.) Depending on where you are in the lifecycle, you can do different things in your code:
-
Read the value of state: When you're in the update process: either in
componentDidMount,componentDidUpdate,render, or a method called by one of those. In any of these parts of the lifecycle, you know that you're guaranteed that state is up-to-date and safe to use. - Change state: In response to an event, like a button click or a text box change. Generally, you only change state from "outside" the lifecycle. Sometimes it's necessary to change state from inside the lifecycle, but be careful that you don't cause an infinite loop, as state changes trigger lifecycle events.
-
Access/modify DOM elements or refs: In the "commit" phase: either
componentDidMountorcomponentDidUpdate, or in an event in which you know for sure that your component has successfully mounted.
In general, think about what each stage in the lifecycle means, and how that might affect which pieces of data are available and safe to use. Also - always do your best to know where you are in the component lifecycle (or if you're completely outside it) for each line of code that you write.
JS / Web Development Tips
This section discusses some basic tips that aren't necessarily React-specific, but can come in handy when developing any kind of website. There are also much more 'optional' - they can be good to read but not all of them are mission-critical for the assignments in this class. (i.e., you can complete all the assignments without writing any CSS, if you want.)
Basic CSS with IDs
CSS, or Cascading Style Sheets is a language for defining styles for a webpage. HTML is designed primarily to describe document structure, not document looks, so CSS exists to allow web designers to customize the look of any element on the webpage. Every element on a webpage has a default set of styles that are part of the browser itself. By writing CSS for your website, you instruct the browser to override its defaults and use your instructions instead when displaying the webpage to the user. CSS can be used to describe anything from font and background color to complex animations and responses to your mouse movement.
CSS can sometimes be frustrating to work with due to the complexity of its layout rules and conflict resolution rules (the "cascading" part of CSS is tricky business). However, when used for small applications like ours, and in a limited way, it can be powerful. The important thing to remember about CSS when taking 331 is this: if you're stuck or are having trouble getting the CSS to behave the way you want to, skip it and come back. For all assignments in this course, we do not care about the looks of your project. As long as the application is usable, you don't need to worry about making it look good. Therefore: if you get stuck with CSS, make sure you complete the rest of the assignment first, before attempting to fix your problem.
CSS is a complex subject that is way beyond the scope of this course or this document. This section exists in an attempt to give you a small amount of useful tips for very basic CSS, to give you some foundation to use it and learn more as needed for your application.
We're going to be discussing a very specific use-case of CSS in this document. (For those with CSS
experience: we're only going to discuss tag and ID selectors, and only a few specific properties.) To
begin: we need to create a CSS document and add it to our React application. To create a CSS document,
simply create a file in src/ that has the .css extension.
Then, To add it to our React application, we import it into our App component. To do
that, add the following line at the beginning of App.js (replace the name of your CSS
file as needed):
import "./App.css";
Now, we can start writing CSS Rules in our new file. Each rule is structured as follows:
selector {
property: value;
property2: value;
...
propertyN: value;
}
A rule is therefore made of two parts: a selector, and a list of property-value pairs. The selector is a notation for describing a specific set of elements on the HTML webpage, and the properties listed within the curly braces are applied to all the elements that match the selector. We can write selectors based off a number of things, but two common ways to "select" elements is by their tag - that is, what kind of element they are, and by their ID - the value of the "id" attribute declared as part of the tag.
Selecting by tag type is easy: simply write the name of the tag. For example, the following rule
applies its property values to all <p> elements:
p {
... /* properties go here */
}
Also, note that CSS allows multi-line comments with /* ... */, but does
not allow comments with // .... For a single-line comment, just write
the text on one line inside /* .... */. Remember that CSS only operates on the generated
HTML - it knows nothing about React - so we can't use names of React components here, just the HTML
tags created by those components' render methods. If we wanted to select a single element
instead of all elements of a particular type, we can do so by selecting that element's ID. To select
an ID, put a "#" symbol directly before the ID. To select the element <p
id="special-paragraph">Some Special Text</p>, you would use the selector:
#special-paragraph { ... }
Since IDs are (supposed to be) unique, using ID selectors allow you to apply styles directly to very
specific parts of your webpage. Also, since any element can have an ID, this allows you complete
control over any element on your page. (There's another way to select groups of elements that should
be styled similarly called 'classes', consult a CSS reference for details on how to use this, we don't
discuss it in this document.) Selectors can also be chained with spaces. Each next piece of the
selector means "inside the previous part." So, #theDiv p { ... } would select Paragraphs
2 and 3 (i.e. "a paragraph tag that appears inside the element with ID 'theDiv'"), but not Paragraph 1
in the following HTML:
<p>Paragraph 1</p>
<div id="theDiv">
<p>Paragraph 2</p>
<div id="someOtherDiv">
<p>Paragraph 3</p>
</div>
</div>
There are many other ways to combine and chain selectors, see a CSS reference for more information. Now that we're able to select elements, what kinds of properties can we apply to them? There are lots of different properties, many of which focus on how an element looks. For the purposes of this document, we'll primarily focus on properties that determine where an element appears on the page, as that tends to be more helpful for 331 students. Every CSS property is written in a rule with the property name on the left, a colon, the property value on the right, and finally a semicolon. Many property values take units, the most common being "px", or pixels. For example, the following rule creates a margin (blank space) of 5 pixels around all paragraph elements, and colors their backgrounds red:
p {
margin: 5px;
background-color: red;
}
There are two primary ways to create space around an element: margin and padding. Their difference is where they put that space: margin add space on the outside of an element's border, while padding adds space inside an element's border, between the border and the content. If you actually draw a border on the element (with the border property) this is most visible, but it can also be noticed if you have a background color for your element, for example. Creating space around elements is useful because, by default, most elements are drawn as close as possible to their neighbors, making for a cramped webpage. Setting the background color of an element can be useful for debugging - to see where an element is on the webpage and how large it is.
One thing to note about margin: the "auto" value can be used to tell the browser to automatically calculate margins. When a browser calculates margins, it attempts to balance the margins so an element is centered. This can be useful to centering elements within their parents.
A (very short) list of useful CSS properties is below, linked to the W3Schools documentation for that property, which discusses the meaning and use of that property as well as what possible values can be assigned to it. See a CSS reference for a complete list (there are LOTS of possible properties).
- text-align Used to align text (left, right, center, etc.) within an element. If the element itself is not aligned, this property will not help. Try setting the margins of that element to align the element relative to its parents.
- border Draws a customizable border around an element, between any padding space and and margin space that the element has. There are lots of different options to choose how the border looks.
- margin Creates an area of empty space around the outside of an element. There are many different forms that allow you to set margins for only certain sides of an element, or to automatically calculate margins to center an element, for example.
- padding Creates an area of empty space inside an element, between the border and the content. The syntax is similar to the margin property, and has many different forms.
- background-color Sets a background color for the element, which is drawn inside the border (i.e. the padding space is drawn with the background color, but the margin space is not).
- color Sets the text color of the text within an element.
- font-size Sets the font size for text within an element.
- width / height Sets the dimensions of an element.
See the following CSS references for complete documentation on what you can do with CSS:
- Selectors: All the different ways to select elements.
- Properties: All the different properties that can be assigned, their possible values, and their meanings.
The Google Chrome developer tools has a sidebar that will show you where all CSS properties come from for an element and which ones are currently active or being overridden. Note: If you attempt to use CSS classes in HTML elements declared with JSX, remember that React renames the "class" attribute to "className".
export default ;
You'll see this line at the bottom of basically every component you write. This allows you to use a simpler version of the "import" statement at the top of other files where you're using that component. If you're having issues importing your components from other files, check to make sure that you are properly "exporting" your component at the bottom of the file in which you define it.
Using Arrow Functions for Callbacks
In Java, the value of the variable this is always well-defined and can never be null,
because the compiler's rules about which code is considered "valid." In Javascript, however, the value
of this is dependent on the context of a function call, and sometimes it's set to undefined.
In certain situations, it can be useful to declare a function using a slightly altered syntax (the
arrow function syntax), as that altered syntax actually has a slightly different meaning in Javascript
and can help prevent this from being undefined when you don't want it to be.
Note that the material discussed below is not something that you need to know, but it can be helpful for debugging and is encouraged if you'd like a better understanding of how your code is working in the Lines and Campus Paths assignments. For a short-and-simple rule of thumb: if you ever pass a function-as-a-value anywhere, or store a function in a variable, you should declare that function using the arrow function syntax instead of the regular function syntax. You'll do this most commonly when you're writing callback functions or event handlers (which are themselves callbacks). This section attempts to explain why the different syntax works, and what's going on inside the code. We're going to discuss what is going on here using the following example code (don't worry about the comments on the last few lines yet, we'll discuss them in depth later):
broken-this.js:
1 class Foo {
2 constructor() {
3 this.greeting = "Hello";
4 }
5 bar = () => {
6 console.log(this.greeting + " bar!");
7 }
8 baz() {
9 console.log(this.greeting + " baz!");
10 }
11 }
12
13 function callFunction(someFunc) {
14 someFunc();
15 }
16
17 let foo = new Foo();
18 foo.bar(); // Works fine! 'this' is based on the value of 'foo'
19 foo.baz(); // Works fine! 'this' is based on the value of 'foo'
20
21 callFunction(foo.bar); // Works fine! 'this' is "remembered" from
// when 'bar' was defined (during the call to 'new')
22 callFunction(foo.baz); // Broken!! 'this' isn't remembered, and 'someFunc()' is called
// without a something.someFunc() attached to it
This declares a simple javascript class called Foo that has a constructor, a property
initialized by that constructor called greeting, and two methods declared in different
ways. bar is declared with the "arrow function" syntax, while baz is a
regular class method. It also declares a standalone function called callFunction that
takes a parameter someFunc that's a function, and calls that function.
As is hinted in the comments on lines 18-22 (which make use of the above class and functions), when we run the following code, the browser console displays this:
Hello bar! Hello baz! Hello bar! Uncaught TypeError: Cannot read property 'greeting' of undefined at baz (broken-this.js:9) at callFunction (broken-this.js:14) at broken-this.js:22
Let's examine why lines 18 and 19 work in more detail. As a Java programmer, it probably seems obvious
that it would work, it's just a normal method call! When those calls are made, the value of
this is determined by the object on which you are calling that method. For lines 18 and
19, we are deliberately calling the bar() and baz() methods on
foo using the dot synax: foo.___(). This is the default behavior for
Javascript: when there's a method call on an object, that object becomes this
for the purpose of the method call.
Line 21 and 22 are where things get more interesting. Let's examine why line 22 fails first, and then
discuss why line 21 gets around this problem, even though they look almost identical. Line 22 begins
by evaluating the value of the function's parameter, which is the expression foo.baz.
That expression evaluates to a function (since foo.baz is a variable in the
foo object, which was defined to hold a function). That function is then put inside the
variable someFunc, and the body of the callFunction function is executed.
callFunction takes the value of someFunc and calls it as though it's a
function (which it is). Notice that, on line 14, there is no dot syntax, nothing like _____.someFunc().
Since at the callsite (the location of the actual function call), there is no
defined object that the function is being called on, this is never set. Therefore, this
stays undefined -- when baz tries to read a parameter of this at line 9, an
error occurs. This is mildly similar to the way you'd expect a static method to behave in Java - when
you call a function without a specific receiver (the object on the left side of the period),
the function is called without this set, as though it's a static function that belongs to
no particular object. When you call it with a receiver, then it behaves like a normal
instance method call, and this is bound appropriately.
You may be thinking "wait, it says foo.baz right there on line 22." That's true, but the
foo. part of that expression only exists on line 22, and it only exists to tell
Javascript where to look for the baz function so it can be passed as a parameter. At the
actual location of the function call, Javascript (more specifically - the callFunction
function) only knows that it's calling the function passed to it; it doesn't know anything about what
object that function may or may not have come from. The key thing to remember is: the value of this
is determined by what is happening at the callsite: if there's a deliberate object that the
function is being called on (receiver), then this is set to that object. Otherwise,
this isn't set. (Actually, that last sentence is usually true but not always. In certain
versions of Javascript and certain environments, this might default to be set to a
different, global object, like window, but that's still a problem because it's definitely
not being set to the Foo object that we need).
So now that we know why line 22 fails, why should line 21 be any different? We're still calling the
function without a receiver - this should be undefined! This is where the
difference between the two kinds of function declarations become apparent. Plain old function
declarations, like the declaration of baz, do exactly what you'd expect: they create a
function that behaves as described above. "Arrow functions," such as how bar is declared,
are a little different. Instead of just creating a plain old function, they make something slightly
more special. It's something that behaves just like a function: you can call it, pass it around, and
get a return value from it. However, it also is capable of "remembering" information about where and
when it was created. One of those pieces of information that it "remembers" is the value of
this. So, the lines 5-7 are actually doing something slightly more special than just
create a function - they're creating an object that acts just like a function, but also remembers
information about where it was declared, and stores that new object into the variable bar.
Computer scientists often call this special object that behaves like a function but can "remember"
extra things a "Closure." (Closures are an extremely powerful feature of many languages, take CSE 341
to study them in depth.)
Now, it starts to make sense why line 21 still works. Even though, at the callsite, there is no object
to set to this for the function bar - it doesn't need it. When
bar was created (on line 17, as part of the creation of the foo object) it
"remembered" what the value of this was. That way, when execution gets to line 6, this
is set to the foo object. Since that's the case, it's perfectly fine to get the greeting
property from inside that object and use it.
So why do we need something like this in the first place? You probably don't have a
callFunction function - it's kinda pointless outside of this example. You do
have something that works similarly, though: event listeners. When you register a callback function
for something like an onClick listener: what you're doing is giving a button
object (or some other kind of UI object) a function for it to save in a variable somewhere. Then, when
it is clicked, it calls that function the same way the callFunction function calls a
function. Since you never gave the button object a reference to the object that it was
supposed to call that function on, it doesn't call it on anything. (You never gave the button
your foo, so it can't say foo.onClick().) If the function was declared
without the "arrow function" syntax, then, it has no way to know what this is, and you
get an error! However, if you were to pass a function that was declared with the "arrow
function" syntax, it would remember what this was without the button needing
to keep track of anything, and everything would work fine!
This is why you see a lot of the sample and starter code using the arrow function syntax instead of
regular functions: many of the functions when designing user interfaces are going to be passed as
values to other functions, and we want to make sure all of our this references work
correctly. Note that none of the example code described here uses React at all either - this is part
of the regular Javascript language, it just so happens that React uses a lot of the Javascript
features like passing functions around that can make some of these more tricky parts of the language
relevant.
JS Comparisons with NaN
In Javascript, numbers are floating point, and many programming languages (including JS) include the
special NaN (Not a Number) value as one of the possible floating point values. It is
important to note that NaN, in JS, is defined to be unequal to everything.
Yes, everything. Even NaN itself. As an example, the following code prints "not equal" to
the console.
if (NaN == NaN) {
console.log("equal");
} else {
console.log("not equal");
}
This means that trying to determine if a value is NaN cannot be done through traditional
comparisons, as any traditional comparisons will always evaluate to be unequal. To properly determine
if a value is NaN, use the Number.isNaN()
function.