Lecture 24 - More SQL
Announcements
Exploration session Thursday May 30th, 4:30 pm on computer networks
Announcing HW 5 - Pokedex 2
In a few days we will be pushing more to the starter repository.
You will get an email... do a
a git pull origin master when you do to get the latest stuff!
CP4 Showcase is out!
Note: You will need log in with your uwid for a few projects that create content (for content moderation).
Today's Agenda
- More PHP/PDO/MySQL connections (with) INSERT
- More database manipulation
Review
Take a moment to review the 4 slides below
- Connecting to the database in general and an example (WPL)
-
try/catchin general and an example
Connecting to a database
To connect to a database you need 4-5 pieces of information:
- host
- port (maybe)
- database name
- the user name for the database
- the database password
Then create a PDO
object to represent the database connection
PDO Connection
To find find out what to use with phpMyAdmin, check out the MAMP WebStart page. For other systems you have to do searching on the web.
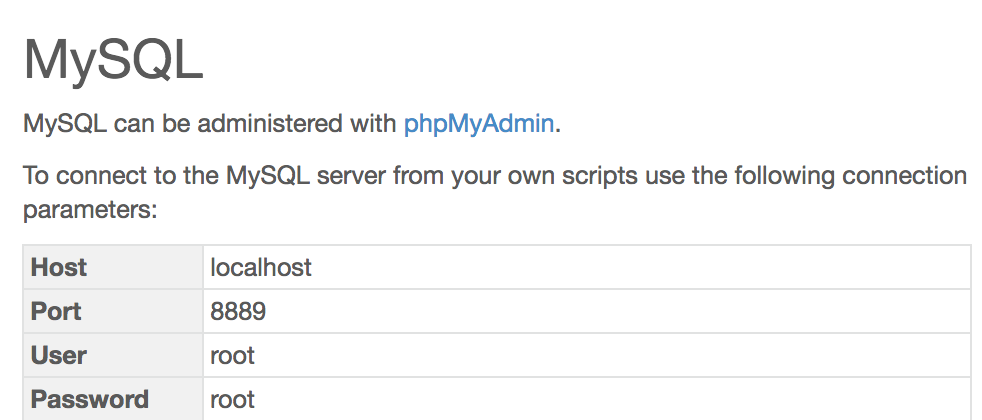
# Variables for connections to the database.
$host = 'localhost'; #fill in with server name
$port = '8889'; #fill in with a port if necessary (will be different mac/pc)
$dbname = 'wpldb'; #fill in with db name
$user = 'root'; #fill in with user name
$password = 'root'; #fill in with password (will be different mac/pc)
# Make a data source string to create the PDO
$ds = "mysql:host={$host}:{$port};dbname={$dbname};charset=utf8";
# connect to the wpldb and set some attributes
$db = new PDO($ds, $user, $password);
$db->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE,
PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION);
PHP (example)
try/catch
Database connections can have different problems: the database server could be down, the database could be missing or corrupted
try/catch helps us catch and
identify when errors occur so we can handle the error correctly
try {
# things to try that could throw an error
}
catch (PDOException $pdoex) {
# code for handling the error here.
}
PHP (template)
try/catch example
try {
$db = new PDO($ds, $user, $password);
$db->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE, PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION);
}
catch (PDOException $pdoex) {
header("HTTP/1.1 503 Invalid Request");
header("Content-Type: text/plain");
die("Can not connect to the database. Please try again later.");
}
PHP (example)
Quickcheck 1
Get in pairs
Partner 1: explain to partner 2 what SQL or MySQL is and how it relates to a full stack applications.
Partner 2: explain to partner 1 what PHP is and how it is used in a full stack application.
Together: Come up with a description of what the PDO object is and represents, why we use it, and what are some of the things we can do with it?
Quick check 2
print("1");
$host = 'localhost';
$port = '8889';
$user = 'root';
$password = 'root';
$dbname = 'wpldb';
$ds = "mysql:host={$host}:{$port};" +
"dbname={$dbname};charset=utf8";
print("2");
try {
$db = new PDO($ds, $user, $password);
$db->setAttribute(PDO::ATTR_ERRMODE,
PDO::ERRMODE_EXCEPTION);
print("3");
}
catch (PDOException $ex) {
die("4");
}
print("5");
PHP
What displays if this script is run and there are no database errors?
1235
What displays if this script is run and there is a database error?
124
What else...
What does a PDO Object encapsulate? a connection to the database
For a valid PDO object $db, what is returned by
$db->query("SQL query string");?
a PDOStatement object
How do you view the rows encapsulated in a PDOStatement? Use...
fetchfetchAllforeachor other type of loop
What do the arrays from PDOStatement::fetch contain? Associations between the column names and data and/or the column positions and the data, by default it's both (PDO::FETCH_BOTH)
What flags can you use to adjust these associations? PDO::FETCH_ASSOC or PDO::FETCH_NUM
PDO and modifying DBs
Remember... With Great Power Comes Great Responsibility
Inserting through PHP
Use the PDO::
exec
function to run a given SQL statement and return the number of rows affected, not
the actual set of results.
$str = "INSERT INTO wpl (name, email, student_id, time, question) " .
"VALUES ('$name', '$email', '$student_id', '$time', '$question');";
$rows = $db->exec($str);
PHP (example)
1PHP (results)
However exec is not secure!!!
It is vulnerable to
SQL injection
(demo)
Little Bobby Tables
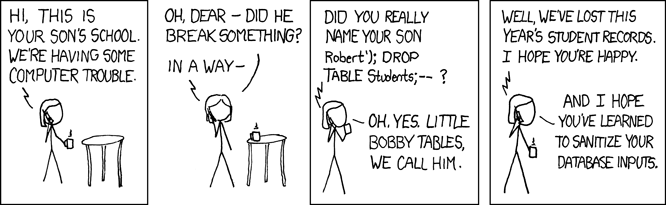
Another example of SQL injection

Using PDO
prepare/
execute for security
$sql = "INSERT INTO queue(name, email, student_id, time, question) " .
"VALUES (:name, :email, :student_id, :time, :question);";
$stmt = $db->prepare($sql);
# create the associative array between the variables in the
# insert SQL statement with the actual values
$params = array("name" => $name,
"email" => $email,
"student_id" => $sid,
"time" => $minutes,
"question" => $question);
$stmt->execute($params); # notice no return value!
PHP (example)
The "variables" with colons in the prepare'd SQL statement are replaced with
values from the associative array that is being passed in to execute
Note: INSERT does not return a set of rows as a result. However, if you
did a query that *does* return a set of rows, you still have to get them from the
$stmt PDOStatement using fetch as before.
prepare/execute
Use prepare/execute whenever there is a "variable"
that is used in a SQL statement will be executed
# This is ok because it does not have any variables it is using in the query
$rows = $db->query("SELECT * FROM queue;");
# This is insecure because it is using a variable that can potentially do
# SQL injection
$rows = $db->query("SELECT * FROM queue WHERE time = {$time};");
# Instead do this:
$sql = "SELECT * FROM queue WHERE time = :time;";
$stmt = $db->prepare($sql);
$params = array("time" => $minutes);
$stmt->execute($params);
PHP
More SQL Commands
DELETE
Deletes the specified records based on the results of the WHERE clause
CAUTION: if you omit the WHERE clause all records will be deleted!!!
DELETE FROM table WHERE condition;
SQL (template)
DELETE FROM queue WHERE id = 8;
DELETE FROM queue WHERE name = "Lauren Bricker";
DELETE FROM queue; # caution!!!
SQL (example)
What if I wanted to delete someone in our WPL queue?
It might help to have this code on your laptop
- What would you want to do to your interface to allow users to easily delete an entry?
- What query statement would you need to delete something from the database?
- What code do you have to modify? What code do you have to create?
- What code could you look at/model after to create your first version of new code?
- How can you test your SQL statements?
- How can you test your PHP code?
- How can you test your JS code/Website?
Demo!
UPDATE
UPDATE table
SET col1 = val1, col2 = val2, ...
WHERE condition;
SQL (template)
UPDATE queue
SET question = "This is a different, harder question"
WHERE id = 4;
SQL (example)
UPDATE changes all rows where the condition is true.
Debugging Strategies
-
Make sure your have the following set in your code
display_errors = on is set in php.ini -
Looking in the
mysql_error_log.errandphp_error.loglog files (C:/MAMP/logs/ on PC or /Application/MAMP/logs on Mac) - Create your own tester program to do GET or POST requests.
- Postman (you need both)