CSE 154
Lecture 2: HTML and CSS
Today's Agenda
Finish HTML tags
Start CSS
Website Organization:
Content and Structure: HTML
Style: CSS
Behavior: JavaScript
Structure of an HTML Page
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
information about the page
</head>
<body>
page contents
</body>
</html>HTML
The <head> tag describes the page and the <body> tag
contains the page's content
An HTML page is saved into a file ending with extension .html
The DOCTYPE tag tells the browser to interpret our page's code as
HTML5, the lastest/greatest version of the language
Page Title: <title>
Chapter 2: HTML Basics
HTML
Placed within the <head> of the page
Displayed in the web browser's title bar and when bookmarking the page, otherwise not visible to the user as page content
Paragraph: <p>
paragraphs of text (block)
You're not your job.
You're not how much money you make in the bank.
You're not the car you drive.
You're not the content of your wallet.
You're not your khakis.
You're not the all-singing, all-dancing crap of the world.
HTML
You're not your job. You're not how much money you make in the bank. You're not the car you drive. You're not the content of your wallet. You're not your khakis. You're not the all-singing, all-dancing crap of the world.
output
Placed in the body of the page
Headings:
<h1>,
<h2>, ...,
<h6>
headings to separate major areas of the page (block)
University of Whoville
Department of Computer Science
Sponsored by Micro$oft
HTML
University of Whoville
Department of Computer Science
Sponsored by Micro$oft
output
<header>
and <footer>
<header> tags usually contain one or more <h1-6>
elements, maybe a logo, and authorship information
<footer> tags might contain site map links, authorship
information, copyright information, etc.
more html elements
...maybe some other stuff...
HTML
These tags are both block elements
Note: not to be confused with the <head> tag, the
<header> is designed to contain headings for a
document.
<article> and
<section>
The <article> tag is a standalone piece of content (eg, entire blog post,
including title, author, etc) (block)
The <section> tag is a piece of content that doesn't make sense on its own
(a chapter, paragraph, etc) (block)
HTML
Horizontal rule:
<hr>
a horizontal line to visually separate sections of a page (block)
First paragraph
<hr />
Second paragraph
<hr>
Third paragraph
HTML
First paragraph
Second paragraph
Third paragraph
output
This is the first example we've seen of a void (self-closing
) tag:
more on HTML Element types
Links:
<a>
links, or "anchors", to other pages (inline)
Search for it on Google!
HTML
Search for it on Google!
output
Uses the href attribute to specify the destination URL
- Can be absolute (to another web site) or relative (to another page on this site)
Anchors are inline elements; must be placed in a block element such as
<p> or <h1>
More About HTML Tags
Some tags can contain additional information calledattributes
- Syntax:
<element attribute="value" attribute="value"> content </element> - Example:
<a href="page2.html">Next page</a>
Some tags don't contain content and can be opened and closed in one tag
- Syntax:
<element attribute="value" attribute="value" /> - Example:
<br />, <hr />, <br>, <hr> - Example:
<img src="bunny.jpg" alt="pic from Easter" /> - Note: whether you use the '/' in a self-closing tag is up to you, as long as you're consistent
Block and Inline Elements (explanation)
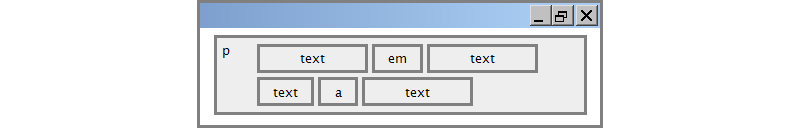
Block elements contain an entire large region of content
- Examples: paragraphs, lists, table cells
- The browser places a margin of whitespace between block elements for separation
Inline elements affect a small amount of content
- Examples: bold text, code fragments, images
- The browser allows many inline elements to appear on the same line
- Must be nested inside a block element
You knew there were going to be rules and exceptions...
Block vs. inline:
-
Some block elements can contain only other block elements:
<body>,<form> -
<p>tags can contain only inline elements and plain text -
Some block elements can contain either:
<div>, <li>
Some elements are only allowed to contain certain other elements:
-
<ul>is only allowed to contain<li>
Some elements are only allowed once per document:
<html><body><head><main>
Images:
<img>
Inserts a graphical image into the page (inline)

HTML

output
The src attribute specifies the image URL
HTML5 also requires an alt attribute describing the image, which
improves
accessibility for users who can't otherwise see it
More About Images
<a href="http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Koala/">
<img src="images/irrelephant.jpg" alt="Irrelephant elephant"
title="dumbo!" />
</a>HTML
If placed in an <a> anchor tag, the image becomes a link
What's the title attribute?
-
titleattribute is an optional tooltip (on ANY element) -
BUT the
titleattribute doesn't always work well for mobile and accessibility, so its usage and future are debated
Line Break:
<br />
forces a line break in the middle of a block element (inline)
The woods are lovely, dark and deep,
But I have promises to keep,
And miles
to go before I sleep,
And miles to go before
I sleep.
HTML
The woods are lovely, dark and deep,
But I have promises to keep,
And miles
to go before I sleep,
And miles to go before
I sleep.
output
Warning: Don't over-use br (guideline: >= 2 in a row is bad, better to not use any)
br tags should not be used to separate paragraphs or used multiple times in a row to create spacing
Phrase elements
:
<em>, <strong>
em: emphasized text (usually rendered in italic)
strong: strongly emphasized text (usually rendered in bold)
HTML is really, REALLY fun!
HTML
HTML is really, REALLY fun!
output
As usual, the tags must be properly nested for a valid page
Nesting Tags
<p>
HTML is <em>really,
<strong>REALLY</em> lots of</strong> fun!
</p>
HTML (bad)
<p>
HTML is <em>really</em>,
<strong>REALLY</strong> lots of</strong> fun!
</p>
HTML (good)
Tags must be correctly nested
- A closing tag must match the most recently opened tag
The browser may render it correctly anyway, but it is invalid HTML
- How would we get the above effect in a valid way?
Comments: <!-- ...
-->
comments to document your HTML file or "comment out" text
<!-- My web page, by Suzy Student
CSE 190 D, Spring 2048 -->
<p>CSE courses are <!-- NOT --> a lot of fun!</p>HTML
CSE courses are a lot of fun!
output
Many web pages are not thoroughly commented (or at all)
Still useful at top of page and for disabling code
Comments cannot be nested and cannot contain a --
Do not leave commented-out HTML code in your homework assignments!
Web Standards
It is important to write proper HTML code and follow proper syntax
Why use valid HTML and web standards?
W3C HTML Validator
HTML
Checks your HTML code to make sure it follows the official HTML syntax
More picky than the browser, which may render bad HTML correctly
Unordered List:
<ul>,
<li>
ul represents a bulleted list of items (block)
li represents a single item within the list (block)
- No shoes
- No shirt
- No problem
HTML
- No shoes
- No shirt
- No problem
output
More About Unordered Lists
A list can contain other lists:
- Simpsons:
- Homer
- Marge
- Family Guy:
- Peter
- Lois
HTML
- Simpsons:
- Homer
- Marge
- Family Guy:
- Peter
- Lois
output
Ordered List: <ol>
ol represents a numbered list of items (block)
RIAA business model:
<ol>
Sue customers
???
Profit!
</ol>HTML
RIAA business model:
- Sue customers
- ???
- Profit!
output
We can make lists with letters or Roman numerals using CSS (later)
Definition list:
<dl>, <dt>, <dd>
dl represents a list of definitions of terms (block)
dt represents each term, and dd its definition
- newbie
-
one who does not have
mad skills
- own
-
to soundly defeat (e.g.
I owned that newbie!)
- frag
-
a kill in a shooting game
HTML
- newbie
- one who does not have mad skills
- own
- to soundly defeat (e.g. I owned that newbie!)
- frag
- a kill in a shooting game
output
Quotations: <blockquote>
a quotation (block)
As Lincoln said in his famous Gettysburg Address:
Fourscore and seven years ago, our fathers brought forth
on this continent a new nation, conceived in liberty, and
dedicated to the proposition that all men are created equal.
HTML
As Lincoln said in his famous Gettysburg Address:
Fourscore and seven years ago, our fathers brought forth on this continent a new nation, conceived in liberty, and dedicated to the proposition that all men are created equal.
output
Inline quotations: <q>
a short quotation (inline)
Quoth the Raven, Nevermore.
HTML
Why not just write the following?
<p>Quoth the Raven, "Nevermore."</p>We don't use " marks for two reasons:
- HTML shouldn't contain literal quotation mark characters; they should be written as
" - Using
<q>allows us to apply CSS styles to quotations (seen later)
HTML Character Entities
a way of representing any Unicode character within a web page
| character(s) | entity |
|---|---|
| < > | < > |
| é è ñ | é è ñ |
| ™ © | ™ © |
| π δ Δ | π δ Δ |
| И | И |
| " & | " & |
- Complete list of HTML entities
- How would you display the text
&on a web page?
HTML-encoding text
<p>
<a href="http://google.com/search?q=marty&ie=utf-8">
Search Google for Marty
</a>
</p>HTML
<p> <a href="http://google.com/search?q=marty&ie=utf-8"> Search Google for Marty </a> </p>
output
To display the link text in a web page, its special characters must be encoded as shown above
Deletions and insertions:
<del>, <ins>
content that should be considered deleted or added to the document (inline)
Final Exam Midterm is on Aug 29
Apr 17.
HTML
Final Exam Midterm is on Aug 29
Apr 17.
output
Abbreviations:
<abbr>
an abbreviation, acronym, or slang term (inline)
Safe divers always remember to check their
SCUBA gear.
HTML
Safe divers always remember to check their SCUBA gear.
output
Computer Code:
<code>
a short section of computer code (usually shown in a fixed-width font)
The ul and ol
tags make lists.
HTML
The ul and ol
tags make lists.
output
Preformatted Text:
<pre>
a large section of pre-formatted text (block)
<pre>
Steve Jobs speaks loudly
reality distortion
Apple fans bow down
</pre>HTML
Steve Jobs speaks loudly
reality distortion
Apple fans bow down
output
Displayed with exactly the whitespace / line breaks given in the text
Shown in a fixed-width font by default
How would it look if we had instead enclosed it in code
tags?
Web Page Metadata:
<meta>
information about your page (for a browser, search engine, etc.)
HTML
Placed in the head section of your HTML
page
meta tags often have both the name and content attributes
- Some
metatags use thehttp-equivattribute instead ofname - The
metatag withcharsetattribute indicates language/character encodings
Using a meta tag Content-Type stops validator "tentatively valid" warnings
Favorites icon ("favicon")
<link href="filename" type="MIME type" rel="shortcut icon" />
HTML (template)
<link href="yahoo.gif" type="image/gif" rel="shortcut icon" />HTML (example)
The link tag, placed in the head section, attaches another file to the page
- In this case, an icon to be placed in the browser title bar and bookmarks
Note for IE6: Doesn't work; must put a file favicon.ico in the root
of the web server (info)
Website organization:
Content and Structure: HTML
Style: CSS
Behavior: JavaScript
The Bad Way to Produce Styles
<p>
<font face="Arial">Welcome to Greasy Joe's.</font>
You will <b>never</b>, <i>ever</i>, <u>EVER</u> beat
<font size="+4" color="red">OUR</font> prices!
</p>
HTML
Welcome to Greasy Joe's. You will never, ever, EVER beat OUR prices!
output
Tags such as b, i, u and font are
discouraged in strict HTML
- Why is this bad?
Cascading Style Sheets (CSS): <link>
<head>
...
<link type="text/css" href="filename" rel="stylesheet" />
...
</head>HTML (template)
<link type="text/css" href="style.css" rel="stylesheet" />
HTML (example)
CSS describes the appearance and layout of information on a web page (as opposed to HTML, which describes the content)
Can be embedded in HTML or placed into separate .css
file (preferred)
Basic CSS Rule Syntax
selector {
property: value;
property: value;
...
property: value;
}
CSS (template)
p {
color: red;
font-family: sans-serif;
}
CSS (example)
A CSS file consists of one or more rules
A rule selector specifies HTML element(s) and applies style properties
- A selector of
*selects all elements
CSS Properties for Colors
p {
color: red;
background-color: yellow;
}
CSS
This paragraph uses the style above.
output
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| color | color of an element's text |
| background-color | background color that will appear behind the element |
Specifying Colors
p { color: red }
h2 { color: rgb(128, 0, 196); }
h4 { color: #FF8800; }
CSS
This paragraph uses the first style above
This h2 uses the second style above
This h4 uses the third style above
output
Color names: aqua, black, blue, fuchsia, gray, green, lime, maroon, navy, olive, purple, red, silver, teal, white, yellow
RGB codes: red, green, and blue values from 0 (none) to 255 (full)
Hex codes: RGB values in base-16 from 00 (0, none) to FF (255, full)
CSS Properties for Fonts
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| font-family | which font will be used |
| font-size | how large the letters will be drawn |
| font-style | used to enable/disable italic style |
| font-weight | used to enable/disable bold style |
| Complete list of font properties | |
font-family
p {
font-family: Georgia;
}
h4 {
font-famiy: "Courier New";
}
CSS
This paragraph uses the first style above
This h4 uses the second style above
output
Enclose multi-world font names in quotes
More about font-family
p {
font-family: Garamond, "Times New Roman", serif;
}
CSS
This paragraph uses the above style
output
Can specifiy multiple fonts from highest to lowest priority
Generic font names:
- serif, sans-serif, cursive, fantasy, monospace
If the first font is not found on the user's computer, the next is tried
Generally should specify similar fonts
Placing a generic font name at the end of your
font-family value ensures that every computer will use a
valid font
font-size
p {
font-size: 14pt;
}
CSS
This paragraph uses the above style
output
- Pixels (px) - e.g., 16px
- Point (pt) - e.g., 16pt
- m-size (em) - e.g., 1.16em
Vague font sizes: xx-small, x-small, small, medium, large, x-large, smaller, larger,
Percentage font sizes: 90%, 120%
font-weight,
font-style
p {
font-weight: bold;
font-style: italic;
}
CSS
This paragraph uses the above style
output
Either of the above can be set to normal to turn them off (e.g., headings)
Body Styles
body {
font-size: 16pt;
}
CSS
To apply a style to the entire body of your page, write a selector for the body (saves you from manually applying a style to each element)
CSS Comments: /* ... */
/* This is a comment.
It can span many lines in a CSS file. */
p {
color: red;
background-color: aqua;
}
CSS
CSS (like HTML) is usually not commented as much as code such as Java
The // single-line comment is NOT supported in CSS
The <-- ... --> HTML comment is also
NOT supported in CSS
Grouping Styles
p, h1, h2 {
color: green;
}
h2 {
background-color: yellow;
}
CSS
This paragraph uses the above style.
This h2 uses the above styles
output
A style can select multiple elements separated by commas
The individual elements can also have their own styles (like
h2 above)
Styles that Conflict
body { color: green; }
p, h1, h2 { color: blue; font-style: italic; }
h2 { color: red; background-color: yellow; }
CSS
This paragraph uses the first style above
This heading uses both styles above
output
When two styles set conflicting values for the same property, the latter style takes precedence
(later we will learn about more specific styles that can override more general styles)
W3C CSS Validator
<p>
<a target="_blank" href="http://jigsaw.w3.org/css-validator/">
<img src="http://jigsaw.w3.org/css-validator/images/vcss"
alt="Valid CSS!" />
</a>
</p>
HTML
Checks your CSS to make sure it meets the official CSS specifications
More picky than the web browser, which may render malformed CSS correctly
More CSS Properties!
CSS properties for text
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
text-align |
alignment of text within its element |
text-decoration |
decorations such as underlining |
text-indent |
indents the first letter of each paragraph |
text-shadow |
a colored shadow near an existing piece of text (CSS3) |
line-height,
word-spacing,
letter-spacing |
gaps between the various portions of the text |
| Complete list of text properties | |
text-align
blockquote { text-align: justify; }
h2 { text-align: center; }
CSS
The Emperor's Quote
[TO LUKE SKYWALKER] The alliance... will die. As will your friends. Good, I can feel your anger. I am unarmed. Take your weapon. Strike me down with all of your hatred and your journey towards the dark side will be complete.
output
Can be left, right, center, or justify
(which widens all full lines of the element so that they occupy its
entire width)
text-decoration
p { text-decoration: underline; }CSS
This paragraph uses the style above
output
Can also be overline, line through, blink or none
Effects can be combined:
p { text-decoration: overline underline; }
CSS
This paragraph uses the style above
output
text-shadow
p {
font-weight: bold;
text-shadow: -2px 5px gray;
}
CSS
This paragraph uses the style above
output
shadow is specified as an X-offset, a Y-offset, or an
optional color
The list-style-type property
ol { list-style-type: lower-roman; }
CSS
Possible values:
none: No markerdisc(default),circle, squaredecimal: 1, 2, 3, etc.decimal-leading-zero: 01, 02, 03, etc.lower-roman: i, ii, iii, iv, v, etc.upper-roman: I, II, III, IV, V, etc.lower-alpha: a, b, c, d, e, etc.upper-alpha: A, B, C, D, E, etc.lower-greek: alpha, beta, gamma, etc.- others:
hebrew, armenian, georgian, cjk-ideographic, hiragana, katakana, hiragena-iroha, katakana-iroha
CSS properties for Backgrounds
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
background-color |
color to fill background |
background-image |
image to place in background |
background-position |
placement of background image within element |
background-repeat |
how background image should be repeated |
background-attachment |
whether background image scrolls with page |
background-size |
how large the background appears behind the element |
background |
shorthand to set all backgroud properties |
| More background properties | |
background-image
body {
background-image: url("paw.jpg");
}
CSS
This is the first paragraph
This is the second paragraph...
It occupies 2 lines
output
Background image/color fills the element's content area
background-repeat
body {
background-image: url("paw.jpg");
background-repeat: repeat-y;
}
CSS
This is the first paragraph
This is the second paragraph...
It occupies 2 lines
output
Can be repeat (default), repeat-x,
repeat-y, or no-repeat
background-position
body {
background-image: url("paw.jpg");
background-repeat: no-repeat;
background-position: 370px 20px;
}
CSS
This is the first paragraph
This is the second paragraph...
It occupies 2 lines
output
Value consists of two tokens, each of which can be top, left,
right, bottom, center, a percentage, or a length value in px,
pt, etc.
Value can be negative to shift left/up by a given amount
Embedding style sheets: <style> (BAD)
<head>
<style type="text/css">
p { font-family: sans-serif; color: red; }
h2 { background-color: yellow; }
</style>
</head>
HTML
CSS code can be embedded within the head of an HTML
file
This is bad style; DO NOT DO THIS (why?)
Inline styles: the style attribute (BAD)
<p style="font-family: sans-serif; color: red">
This is a paragraph</p>
HTML
This is a paragraph
output
Higher precedence than embedded or linked styles
Used for one-time overrides and styling a particular element
This is bad style; DO NOT DO THIS (why?)
Content vs. Presentation
HTML is for content; what is on the page (heading; list; code; etc.)
CSS is for presentation; how to isplay the page (bold; centered; 20px margin, etc.)
Keeping content separate from presentation is a very important web design principle
If the HTML contains no styles, its entire appearance can be changed
by swapping .css files
See also: CSS Zen Garden
Cascading Style Sheets
It's called Cascading Style Sheets because the properties of an element cascade together in this order:
- Browser's default styles (reference)
- External style sheets (in a
<link>tag) - Internal style sheets (in a
<style>tag in the page header) - Inline style (the
styleattribute of an HTML element)
Inheriting styles (explanation)
body { font-family: sans-serif; background-color: yellow; }
p { color: red; background-color: aqua; }
a { text-decoration: overline underline; }
h2 { font-weight: bold; text-align: center; }
CSS
This is a heading.
A styled paragraph. Previous slides are available on the web site.
- a bulleted list
output
When multiple styles apply to an element, they are inherited
A more tightly-matching rule can override a more general inherited rule
Not all properties are inherited (notice link's color above)
CSS pseudo-classes
a:link { color: #FF0000; } /* unvisited link */
a:visited { color: #00FF00; } /* visited link */
a:hover { color: #FF00FF; } /* mouse over link */
CSS
output
| Class | Description |
|---|---|
| :active | an activated or selected element |
| :focus | an element that has the keyboard focus |
| :hover | an element that has the mouse over it |
| :link | a link that has not been visited |
| :visited | a link that has already been visited |
| :first-letter | the first letter of text inside an element |
| :first-line | the first line of text inside an element |
| :first-child | an element that is the first one to appear inside another |
| :nth-child(N) | applies to every Nth child of a given parent |



